Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Manufacturing Transactions Guide

Manufacturers and EDI go quite well together. There are two main portions within a manufacturer's EDI business, whether it's conducting direct transactions with wholesalers to integrate into an ERP, or as an e-commerce platform for end consumers. While those are the most recurring ways a manufacturer might utilize EDI, there are actually many EDI manufacturing transactions that companies must manage daily.
But first, let's take a little refresher on the technology that is EDI.
What is EDI?
EDI or Electronic Data Interchange is a technology that has been around for quite some time now. It is the foundation that many businesses rely on in order to better serve their customers, trading partners, and other members of a digital ecosystem. Companies use EDI software to exchange business documents digitally through a standardized format. EDI connects directly from one business to another through e-commerce platforms or ERP systems.
The most common type of digitally transmitted documents can be found in the EDI order processing cycle: purchase orders, invoices, and advanced shipping notices.
EDI is so widely used because it provides reliable communications that all companies, no matter the industry, require.
History of EDI in Manufacturing
Manufacturers continue to utilize EDI because of the numerous benefits the industry has gained over the years by using the technology. It's reliable. The reality is that manufacturers cannot afford to delay onboarding a new trading partner, or connecting to suppliers, logistics companies, or distributors. Modern EDI providers improve supplier and partner onboarding and more.
Manufacturing goods within the United States (as well as Europe) has become expensive, so the need for a modernized EDI solution that streamlines partner onboarding has never been more critical. Being able to connect any type of data or information rapidly is necessary for success for manufacturers of any kind. Additionally, manufacturers must be able to scale as needed and have the flexibility to change up their EDI systems whenever they need to. Some of the other benefits manufacturers gain from EDI include:
- Reduce chargebacks for data exchange errors
- Increase EDI visibility and monitoring across their digital ecosystem
- Reduce costs for operational maintenance and annual support of legacy and/or end-of-life solutions
On top of those features, modern EDI allows manufacturing companies to increase business efficiency through automated transaction workflows, reduce dependencies on manual data entry, save money to avoid EDI chargebacks and SLA violations, and expedite order-to-cash, procure-to-pay, and load-tender-to-invoice processes.

See Our Platform in Action
Watch a quick demo to learn how you can automate EDI & API, onboard parters faster, and directly integrate into any ERP/TMS/WMS.
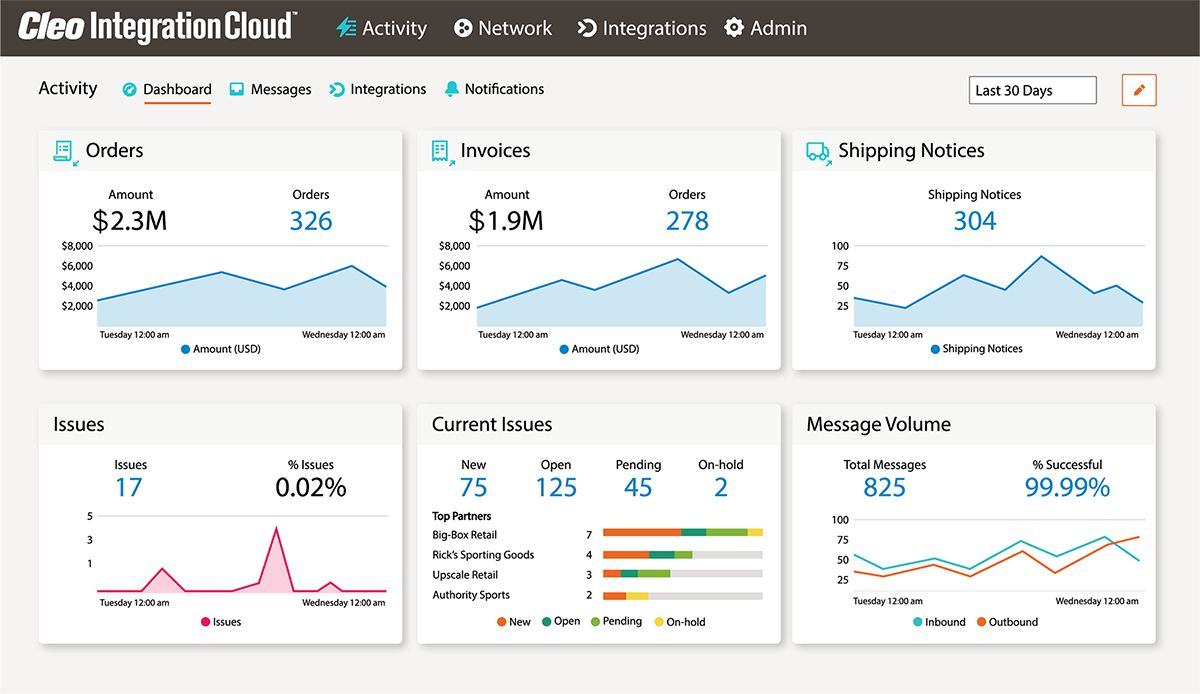
See a screenshot of a Manufacturing EDI transaction set on the Cleo Platform:
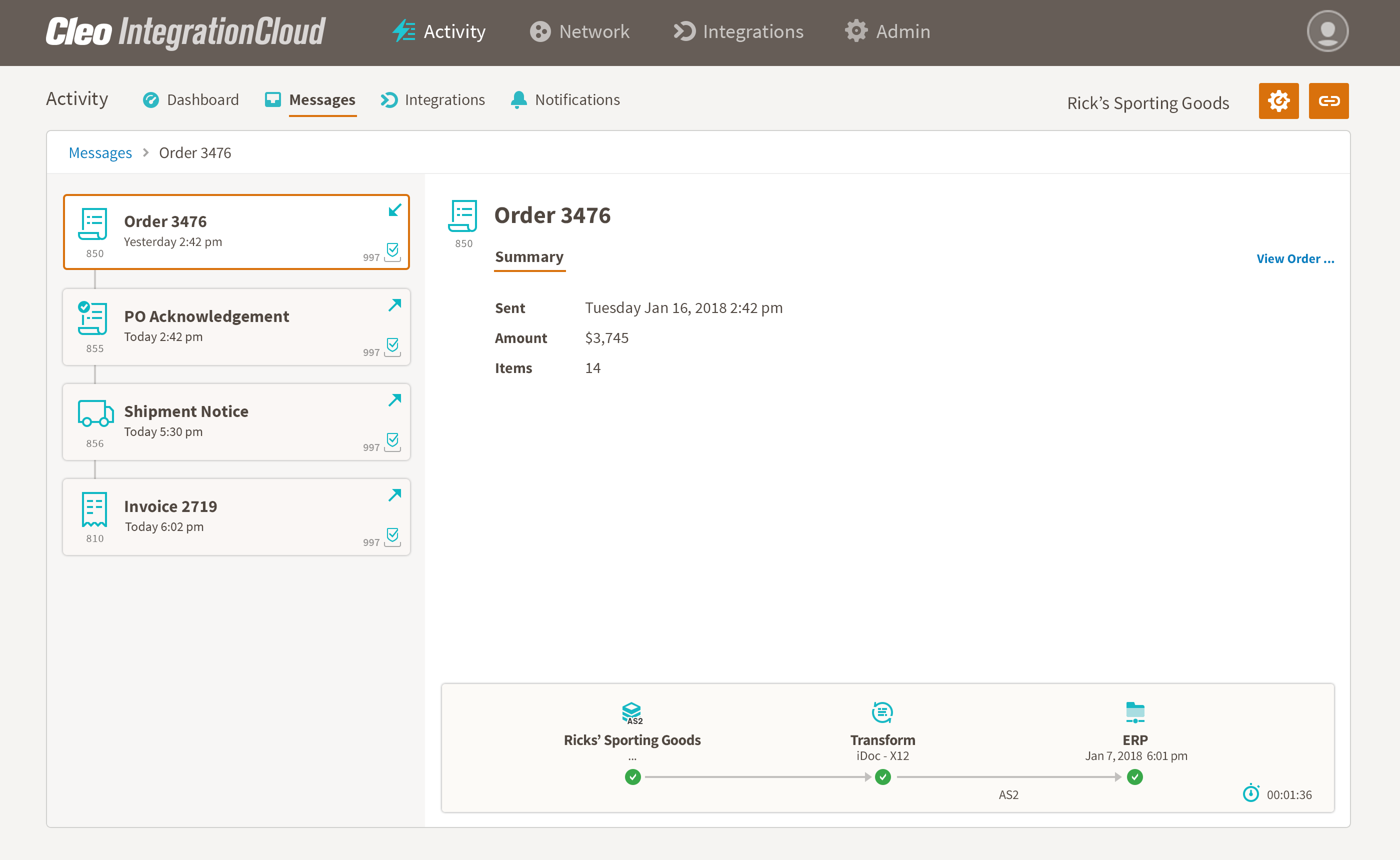
Frequently Used EDI Transactions for Manufacturing
There are many recurring and common EDI transactions that manufacturers most often utilize. As manufacturing EDI transactions can become overwhelming to sort through, we've made it easy for you. Here the most frequently used EDI transactions for manufacturing:
- Sent by a manufacturer to the customer in order to bill for goods ordered and services provided
EDI 830 - Planning Schedule/Material Release
- Sent by a manufacturer to communicate with suppliers. The EDI 830 provides forecast data for upcoming orders that help a supplier manage materials and labor to fulfill orders automatically based on the manufacturer's inventory levels. Manufacturers with EDI 830 material release capabilities often include resource authorizations, period-to-date cumulative quantities, and shipping or delivery patterns for weekly, monthly, or quarterly requirements. EDI 830's with a Material Release can even eliminate the need for the customer to generate separate Purchase Orders
- Sent by a manufacturer to retailers, distributors, dealers, and other members of a trading partner network to provide product information in the form of a catalog. An EDI 832 can be updated in real-time, which allows for accurate product and pricing information, a clear and obvious benefit over a paper catalog
EDI 846 - Inventory Inquiry/Advice
- Sent by a manufacturer to notify retailers, distributors, dealers, and other members of a trading partner network, of on-hand and future inventory levels. EDI 846's have become commonplace in e-commerce order fulfillment, specifically for dropshipping. EDI 846's are becoming a strong requirement to trade with online retailers
- Sent by a manufacturer to purchase materials and/or services from a supplier. EDI 850's generally provide information on the item, price and quantities ordered, shipping details, payment terms, and discounts
EDI 855 - Purchase Order Acknowledgment
- Received by manufacturers to confirm the successful reception of an EDI 850. The EDI 855 communicates whether the EDI 850 was accepted or rejected, or what changes may have been made to accept the order by the supplier or seller
EDI 856 - Advanced Ship Notice
- Sent or received by manufacturers. An EDI 856 is received by manufacturers as notice of an impending physical receipt of material or goods from a supplier. An EDI 856 can also be sent by a manufacturer as a response to an EDI 850, EDI 830, EDI 862 transactions. The EDI 856 details the contents of the shipment, order information, description of products, types of packaging used, carrier information, and more
EDI 860 - Purchase Order Change
- Sent or received by a manufacturer to request a change to a purchase order. The EDI 860 can also be used by buyers to confirm their acceptance of changes to purchase orders made by the sellers
- Sent by a manufacturer to request a supplier to schedule a shipment against an order. An EDI 862 provides detailed shipping requirements and may be triggered by-product usage, allowing suppliers to replenish items immediately, in support of Just-In-Time manufacturing procedures
EDI 940 - Warehouse Shipping Schedule
- Sent by a manufacturer to authorize a warehouse or any other Third Party Logistics Provider (3PL) to make a shipment to a buyer, such as a retailer. The EDI 940 may also be used to confirm a shipment. Manufacturers essentially use the EDI 940 to instruct the warehouse or 3PL on what to ship, how much, and when
EDI 943 - Warehouse Stock Transfer Shipment Advice
- Sent by a manufacturer to a remote warehouse as an advanced shipping notice of a transfer shipment that has been made from the manufacturer. The EDI 943 can also be used by manufacturers to authorize a warehouse to accept a return from a customer. The EDI 943 differs from an EDI 856 Advanced Ship Notice, in that it is specifically for shipments to third-party warehouse locations
EDI 944 - Warehouse Receipt Advice
- Received by a manufacturer and sent by a 3PL provider or warehouse. The EDI 944 is an acknowledgment of receipt of a shipment at the warehouse. The EDI 944 is generally sent following the sending of an EDI 943. The two are generally found in the same sequence with the EDI 943 proceeding the EDI 944
EDI 945 - Warehouse Ship Advice
- Received by a manufacturer and sent by a 3PL provider or warehouse. The EDI 945 is used by a trading partner informs manufacturers that goods or materials have been shipped to a customer. It notifies the manufacturer the shipment was made
EDI 997 - Functional Acknowledgment
- Received by a manufacturer and sent by a customer as an acknowledgment of the receipt of an EDI transactions
While these are the most commonly used manufacturing EDI transactions, the technology has grown so much that there are endless ways for a manufacturer to take advantage of it, especially through a centralized integration platform designed to advance manufacturers' EDI capabilities, keep them competitive in the era of cloud-driven marketplace change, or workaround unforeseen supply chain disruptions. Modern EDI tools are essential for manufacturers to improve communication with customers, onboarding, and overall supply chain agility. Companies that have yet to upgrade their EDI platform are missing out on all the benefits outlined above - and much more.
Want to learn more about modernizing your EDI?
Tour our platform

About Cleo