EDI Order Processing: Automate the EDI Purchase Order Process
A lot of companies are embarking on eCommerce-focused digital transformation initiatives to improve their supply chain agility, especially in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic. Yet in doing so, many overlook the integration fundamentals that can make all the difference in best serving customers, scaling operations, and forestalling disruption.
Let's take EDI order processing as an easy example because it's so critical to delivering the trust-based experience your customers and B2B partners have come to expect.
What is EDI Order Processing?
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) order processing is the process of receiving, processing, and fulfilling purchase orders in a standardized electronic format. EDI order processing allows trading partners / business partners to exchange purchase order information electronically, eliminating the need for manual data entry and paper-based documents.
Here is how it works:
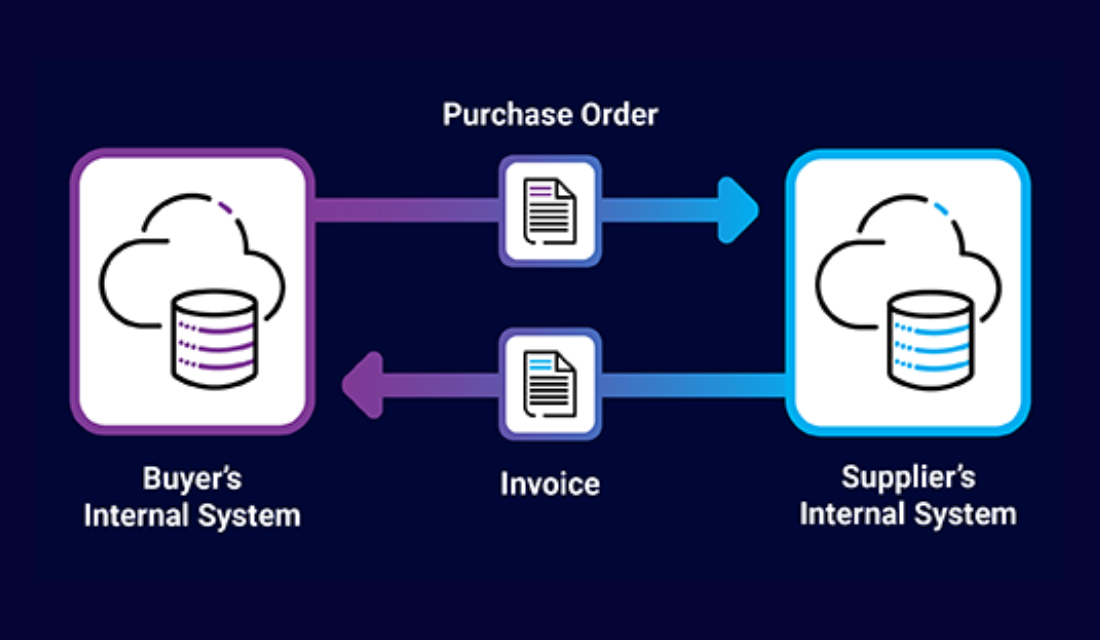
1. The buyer (retailer, wholesaler or distributor) sends an electronic purchase order to the supplier in an EDI format.
2. The supplier's EDI system receives and translates the electronic purchase order (typically using an EDI software platform).
3. The supplier sends an EDI shipping notice when the order is shipped, followed by an EDI invoice to the buyer.
EDI 850 Purchase Order
EDI 850 is an electronic data interchange transaction used to send a purchase order from a buyer to a seller or supplier. Buyers use this document to place orders electronically rather than via email, fax, or phone.
The electronic purchase information includes items being purchased, the quantity and price of each item, as well as the delivery date and location.
As a rule, EDI order processing allows for a far shorter cycle than traditional, paper-based processes that require manual intervention.
Here is what an order processing sequence would be like at a high level:
1. A buyer chooses to purchase a service or good.
2. The automated EDI system used by the buyer creates an EDI version of a purchase order for the product and then sends the order to the supplier.
3. The supplier's order management solution consumes the order and its own systems.
4. The supplier's order management solution will then create an acknowledgment and an invoice and then the supplier's EDI provider will transmit both documents to the buyer to confirm the reception of the purchase order and provide a receipt for the order.
Now here is how the process is conducted using the EDI transactions that correspond to each step of the purchase order process.
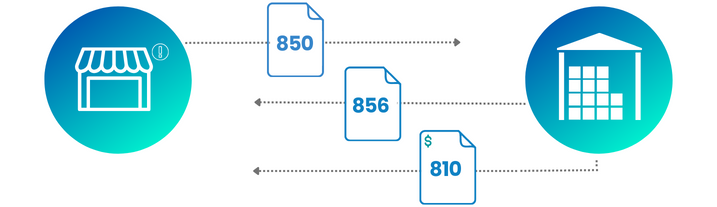
- An EDI 850 Purchase Order is received and accepted from a buyer
- An EDI 855 Purchase Order Acknowledgment is sent to the buyer to confirm the EDI 850 was received
- An EDI 856 Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN) is generated and sent to the buyer describing the contents of each shipment and item packaging details
- An EDI 810 Invoice is created and sent to the buyer
Most Common EDI Order Types Used in the EDI Process
Many major global corporations necessitate the utilization of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transactions for their business operations. Walmart mandates the use of EDI transactions through AS2, requiring all potential business partners to possess EDI capabilities. Similarly, companies like Amazon have established strict vendor criteria that must be met for electronic data interchange.
Below are 7 prevalent EDI order types with examples in the EDI process.
1. EDI 850: Purchase Order
- Example: This is an electronic initiation of a purchase, outlining the items and quantities needed.
2. EDI 855: Purchase Order Acknowledgment
- Example: Sent by retailers to confirm the receipt of a purchase order, detailing accepted quantities, prices, and delivery information.
3. EDI 856: Advanced Ship Notice/Manifest
- Example: This type of EDI is used to provide advanced information about the goods that have been shipped.
4. EDI 810: Invoice
- Example: It involves the electronic submission of invoices for goods or services provided.
5. EDI 820: Payment Order/Remittance Advice
- Example: Suppliers use this to provide payment details, such as amounts and dates, in response to an EDI 810 Invoice.
6. EDI 940: Warehouse Shipping Order
- Example: This EDI type specifies shipping details for warehouse orders, facilitating efficient logistics and delivery processes.
7. EDI 997: Functional Acknowledgment
Example: It acknowledges the receipt and processing of EDI transactions, ensuring their successful transmission.

Level Up Your Supply Chain: Explore Our EDI Solution
You’ve taken the first step towards a smoother supply chain by finding this blog - now discover how our EDI solution automates data exchange, saving you time and boosting efficiency.
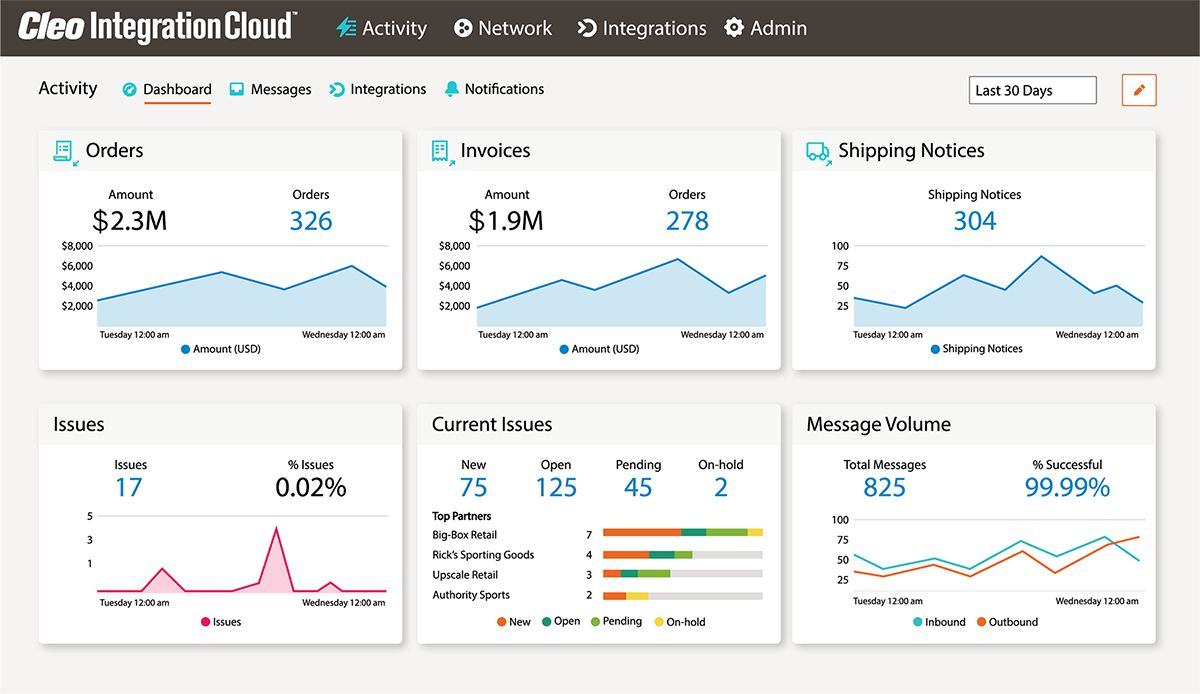
EDI Orders
Here you can see the EDI order format within the Cleo EDI interface screenshots below. You will notice in the bottom portion the EDI documents are being sent and received by your own ERP, which is connected via EDI integration.
First, your EDI 850 purchase order is received from an EDI trading partner (Rick's Sporting Goods).
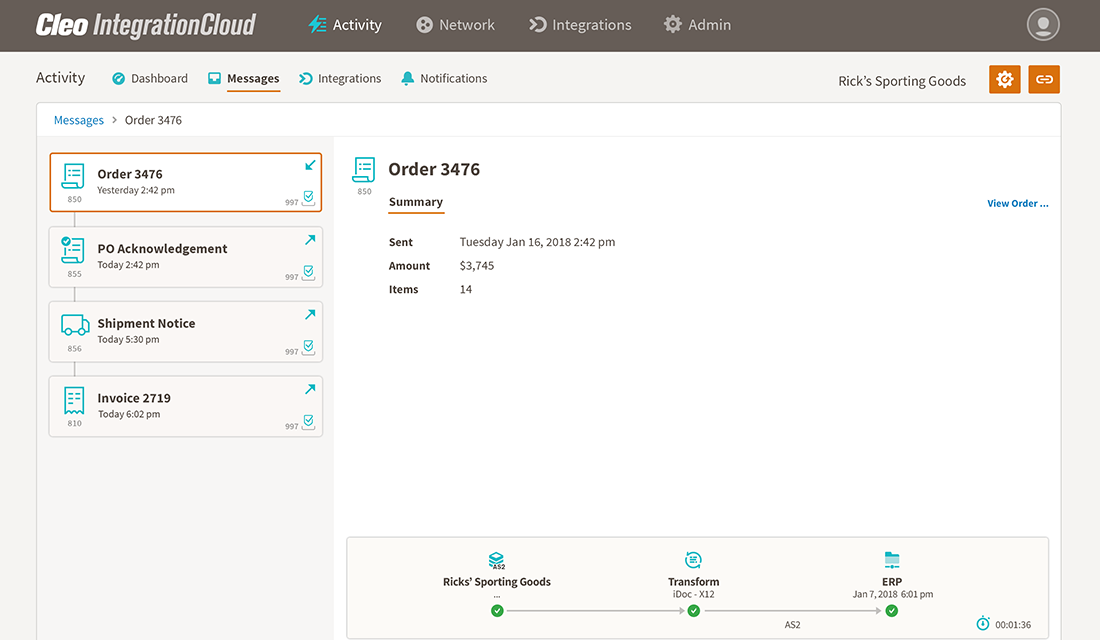
Second, your Cleo EDI Platform creates and sends an EDI 855 Purchase Order Acknowledgment to Rick's Sporting Goods to acknowledge that the EDI 850 purchase order was received.
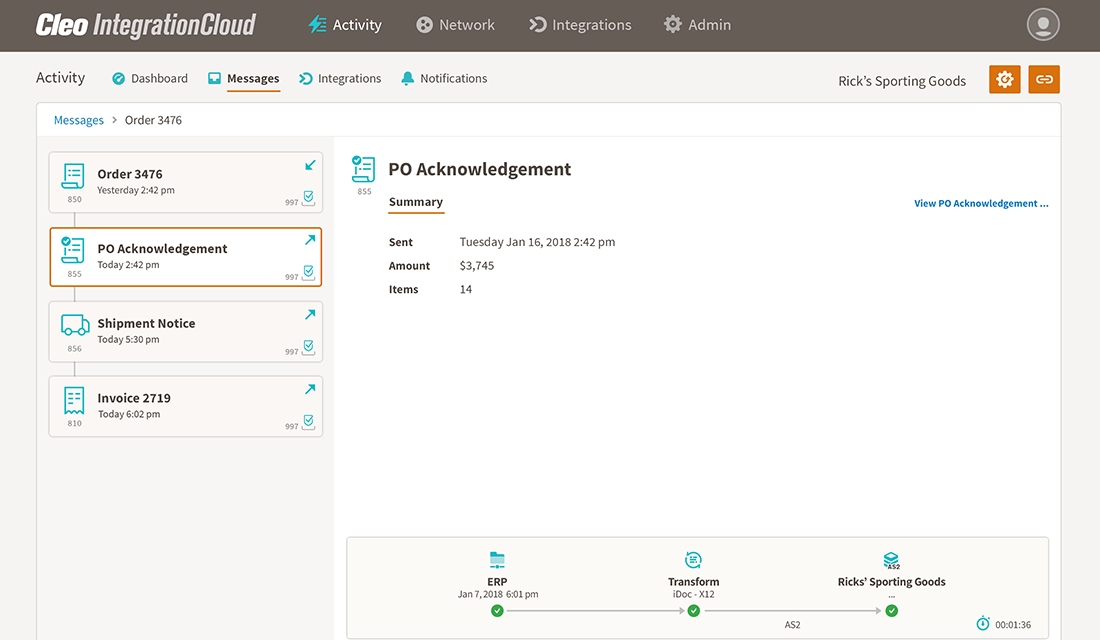
Third, Cleo's cloud-based EDI platform generates an EDI 856 and then sends the document to Rick's Sporting Goods, giving information on the contents of the shipment.
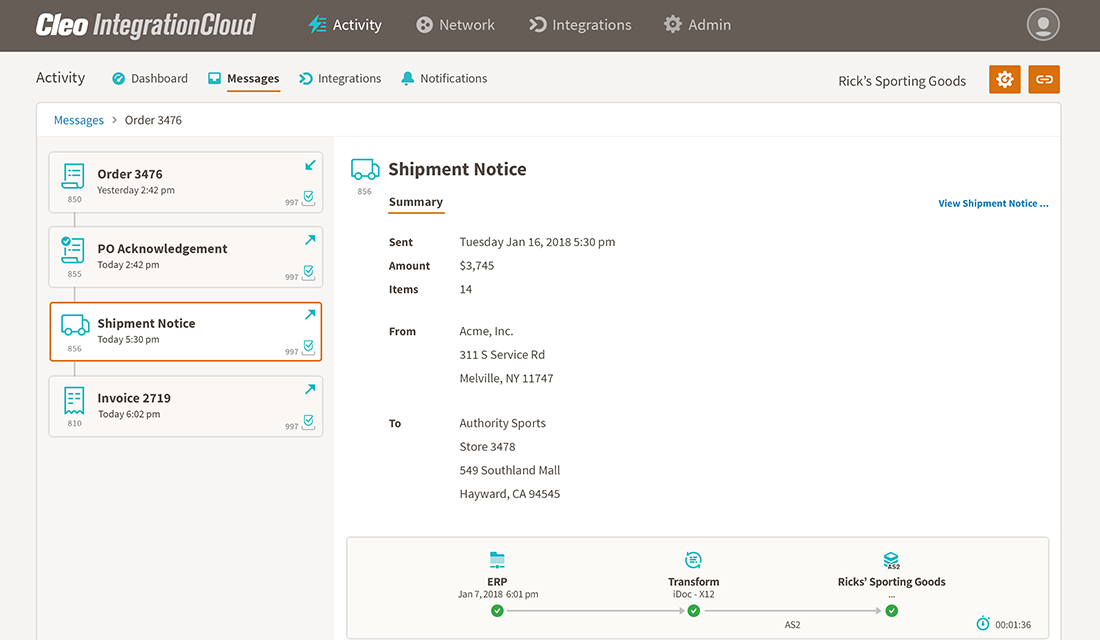
Lastly, Cleo Integration Cloud generates an automated EDI 810 invoice and sends it to Rick's Sporting Goods.
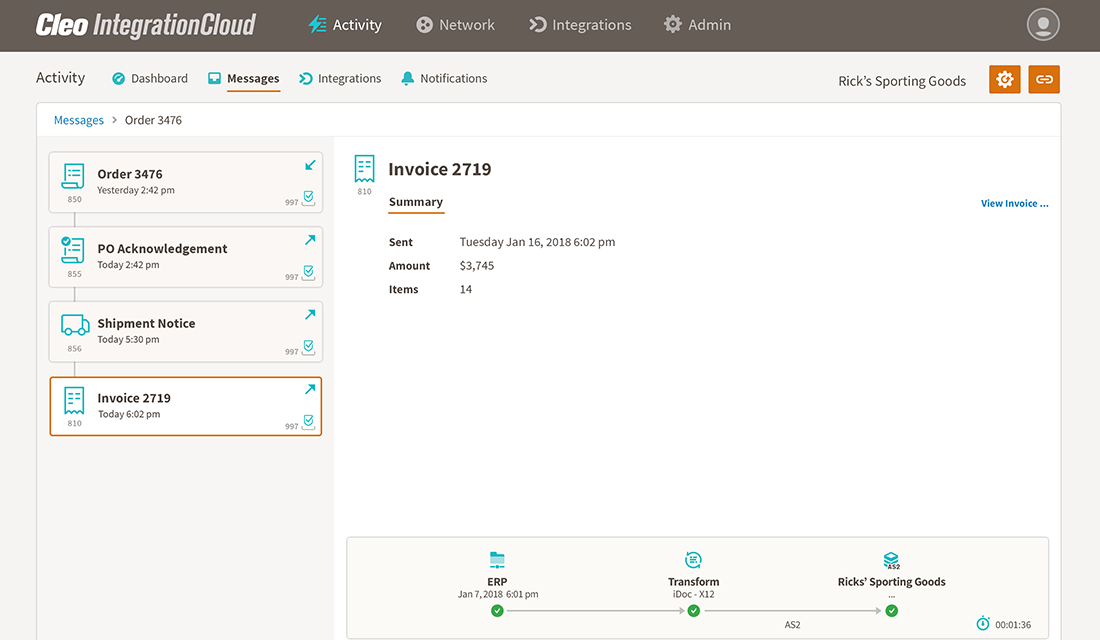
The Value of Automated EDI Order Processing
EDI has been around for years, so long in fact that pretty much any retailer, supplier, carrier, or shipper worth its salt relies on EDI mapping to move orders through the supply chain. It's a lot less cumbersome, faster, and more accurate than relying on manual processes (i.e. processing invoices or purchase orders manually), plus, since so many supply chain players are super familiar with it, it's practically the price of entry to conducting digital commerce these days.
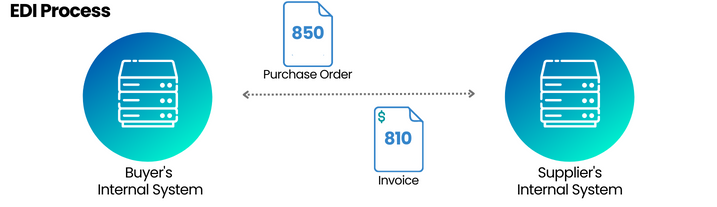
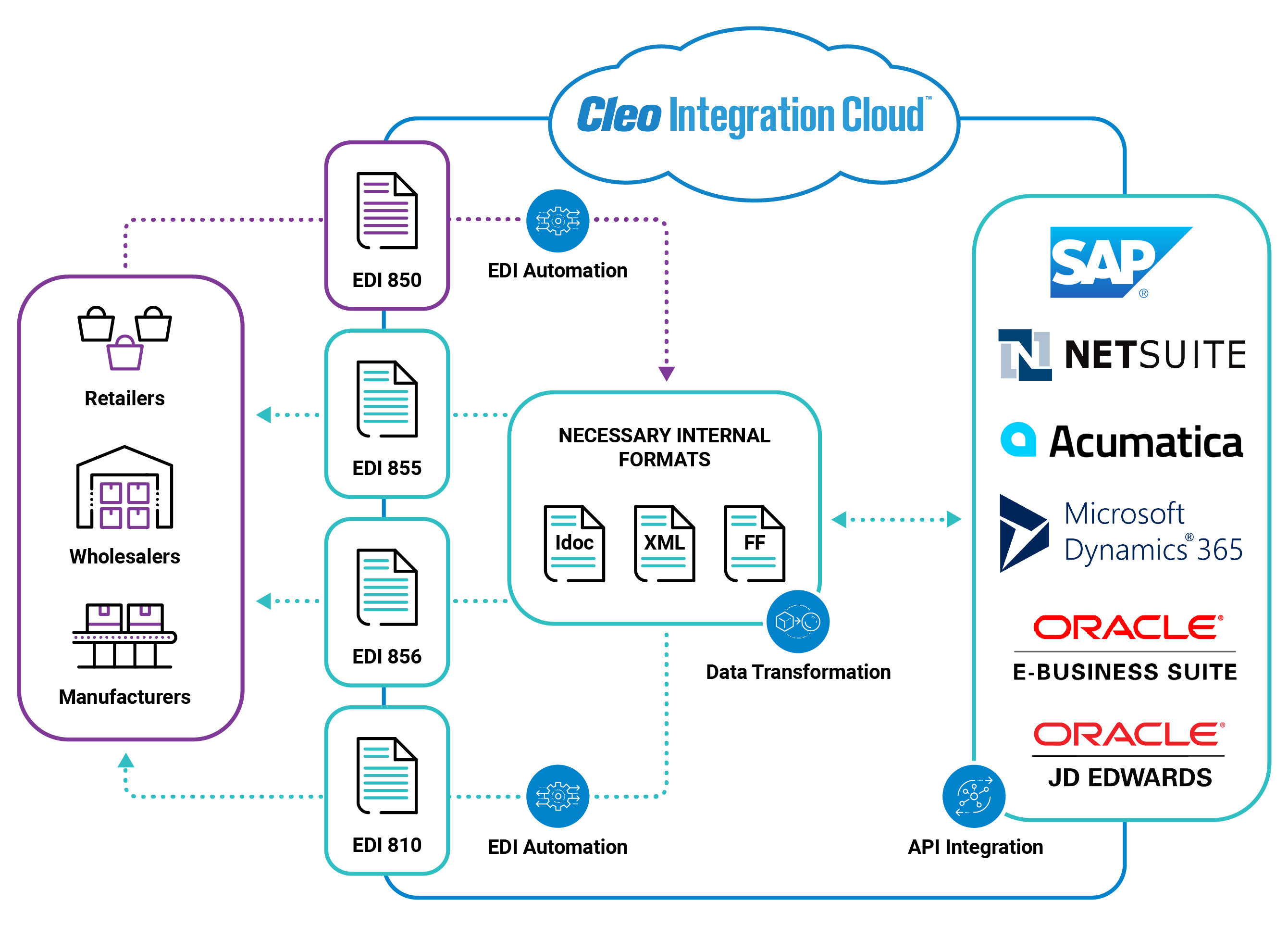
At a high level your EDI order processing should look something like this diagram:
From left to right, you can see and EDI Order cycle in full motion, starting with an EDI 810 being sent from an external trading partner, then the 810 being converted to an internal file format, and finally ingested into a back-end ERP system.
Of course, you can see that same process in reverse as the EDI 855, 856, and EDI 810 are sent to the trading partner, after originating in your back-end system.
What a lot of companies don't know, however, is that EDI order processing and successful eCommerce initiatives are inextricably linked. And it's become about far more than assigning someone to perform simple order entry in your EDI system or working to solve a pesky fulfillment problem.
Because multi-enterprise ecosystems are rapidly expanding in the so-called "new normal," demand-driven post-Covid world, what EDI is really about is supporting end-to-end visibility across such mission-critical business processes as Order-to-Cash, Procure-to-Pay, or Load Tender-to-Invoice.
But why do you need that visibility? Because if you can't efficiently process orders in real time- of whatever kind -- for customers, suppliers, carriers, or shippers, or if your process is too slow or error-prone, competitors who are aggressively digitalizing their companies' operations, will surely pass you by.
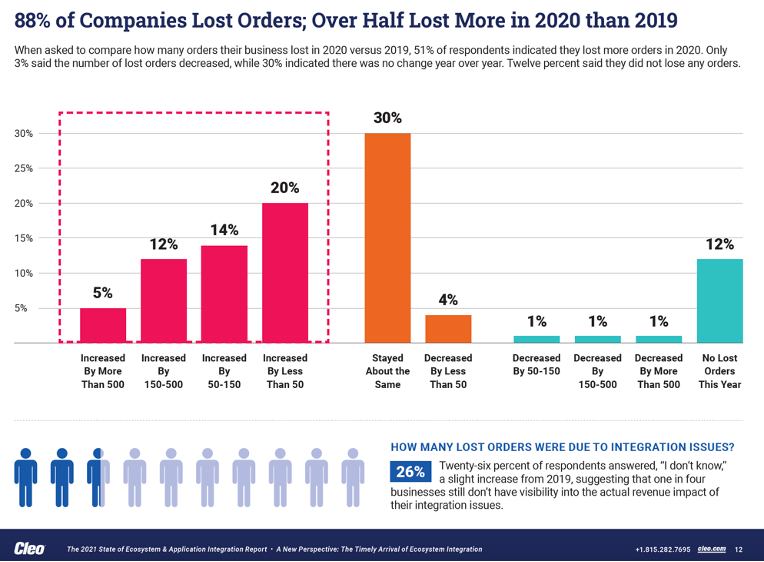
In 2020, 88% of companies surveyed admitted they lost orders, and more than half said they lost more orders in 2020 than in the previous year. 25% said they really don't know how many orders they are losing! Problems like lost orders not only negatively impact the customer experience, they also can cost real money. According to the same survey, 74% of companies indicated they lost more revenue due to integration issues in 2020 than in 2019, with nearly 10% losing one million dollars or more.
Put another way, automating your EDI order process is really more about achieving business outcomes than it is about the software per se.
Beyond Streamlining Orders: Additional Considerations for EDI Order Processing
This blog highlights the benefits of EDI order processing. However, as you consider implementing it, further questions might arise:
1. How can I integrate EDI order processing with my existing business systems, such as my ERP or CRM?
For seamless operation, integrating EDI order processing with your existing software is crucial. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Compatibility: Ensure your chosen EDI provider offers solutions compatible with your existing ERP and CRM systems.
- Data mapping: Define how data will flow between your EDI system and other software. This involves mapping data fields and formats to ensure seamless exchange.
- Implementation expertise: Look for an EDI provider with experience integrating with your specific ERP and CRM systems, ensuring a smooth and efficient implementation process.
By addressing these aspects, you can ensure that EDI order processing seamlessly integrates with your existing software landscape, creating a unified and efficient workflow.
2. What are the different levels of automation possible with EDI order processing, and how can I determine the level that best suits my needs?
EDI order processing offers various levels of automation, impacting workflow and resource requirements:
- Basic automation: Automates tasks like order creation and data validation, reducing manual effort but may require human intervention for order approvals or exceptions.
- Advanced automation: Automates additional tasks like inventory checks, shipping confirmations, and invoice generation, minimizing human involvement and streamlining the order fulfillment process.
- Full automation: Achieves complete automation from order receipt to invoice processing, requiring minimal human intervention, suitable for businesses with high-volume, standardized orders.
The ideal level of automation depends on your business needs, order complexity, and desired level of control. Evaluating these factors will help you choose the most suitable option for your specific situation.
3. How can I measure the success and impact of implementing EDI order processing on my business?
Measuring the success of your EDI implementation is essential to demonstrate its value and identify potential areas for improvement:
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs): Monitor metrics like order processing time, order accuracy, inventory turnover, and customer satisfaction to quantify the impact of EDI on your business performance.
- Compare data before and after implementation: Analyze data trends to assess how EDI impacted processing times, error rates, and overall efficiency.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders: Involve employees and customers in the evaluation process. Collect feedback on their experience with the new system and identify areas for further optimization.
By proactively measuring success through a combination of data analysis and stakeholder feedback, you can ensure that your EDI implementation continues to deliver value and optimize your order processing operations over time.
Remember, EDI order processing offers significant benefits, but addressing integration challenges, choosing the right level of automation, and measuring its impact are crucial for a successful and impactful implementation.

Ready to Take Your EDI Research to the Next Level?
You've explored the benefits, now see how it applies to you! Get a personalized consultation on how our EDI solution can streamline your supply chain. Just provide some information for a free, no-obligation assessment.
How to Choose the Right EDI Solution
So if you're embarking on an electronic data interchange edi initiative, don't take a piecemeal approach that only considers individual parts like your EDI Purchase Order process, or your invoices, or shipping orders. Instead, think holistically and bigger picture. Follow the flow of money into and out of your company and identify -- from a business value perspective -- where your EDI order processing and fulfillment capabilities can be improved.
For starters, here are three desirable business outcomes to ask potential vendors about when shopping for a modern integration solution. By addressing these strategic outcomes from the outset, you'll naturally ensure your company's supply chain is primed to meet anything that comes your way, and you'll position your company for rapid scalability as your business ecosystem grows
- Can you help us improve our customer experience? - For years now, Amazon has been teaching us that ultimately all that matters in this digitally driven world is the customer experience. By taking cues from what this global giant has achieved, every company can continuously improve on how their digital systems shift and evolve to accommodate customers' ever-changing expectations. The key is having a complete and flexible integration solution that gives your supply chain the adaptability and agility to turn on a dime. An EDI-related breakdown at any integration juncture impacts the customer/supplier experience, and can result in lost orders, lost revenue, or worse, broken relationships.
- Can you help us do more business faster and position for rapid scalability? - Truth be told, EDI alone is not enough. With the advent of the cloud and the escalating pace of digital transformation, we're now living in an API-first universe. So, if your company intends to scale up and ride today's global eCommerce wave, you'll need the ability to accommodate both API and EDI integration workflows equally flawlessly, ideally building these capabilities on a single platform that enables you to simultaneously manage both. You'll want your integration solutions to mature as your business grows - technology advances never stop -- so it's probably better to look for an integration platform that puts you in the driver's seat, enabling your business to scale up as needed as your multi-enterprise ecosystem evolves.
- Can you get me the visibility required to forestall supply chain disruption? - When integration technology is working seamlessly across your end-to-end processes - including all the internal and external connections comprising your EDI order processing scheme -- data moves fluidly, all document types are accommodated (automatically transformed when necessary), and what's happening at every key integration point can be seen, understood, and easily controlled. Only an integration approach that considers your business processes end-to-end, starting from an "outside-in" point of view, will be able to connect the complex constellation of internal and external systems and applications you'll encounter with your eCommerce initiative. If you have clear visibility and control, then whenever disruption hits or a business change is mandated, your overall integration solution can readily accommodate the shift in strategy.
For a step-by-step walk through on choosing the right solution, access our (ungated) guide.
As is often said, better planning results from the beginning with the end in mind. So, if you believe your task is to improve your EDI order processing through automation, raise your sights to ask what the real business problems are that you need to solve. Over the longer term, you'll be glad that you did. You'll have more satisfied customers, be able to scale up to capitalize on eCommerce-driven growth and be adequately prepared for any supply chain disruption that comes your way.
Wondering where to start on your eCommerce / supply chain / EDI journey? Connect with our team of EDI experts to discuss your specific pain points and EDI processing needs.

About Cleo