What Is SAP EDI? Best Practice Guide to Automated EDI

Electronic data interchange (EDI) and the SAP enterprise resource planning (ERP) system have both stood the test of time and continue to play crucial roles in modern business operations. With EDI facilitating the automation and streamlining of supply chain management, and SAP providing a suite of integrated applications for managing various business processes, their integration proves to be a powerful combination.
This article will delve into how SAP ERPs and EDI work together, the advantages, challenges, and best practices of successfully integrating EDI and SAP, common SAP EDI transactions, and more.
- What Is SAP EDI?
- What Are SAP's Outbound and Inbound EDI Mapping Processes?
- How Does EDI Work?
- SAP EDI Architecture
- Should You Use SAP's EDI or a Separate EDI Solution?
- Common SAP EDI Transaction Codes
- EDI Integration in SAP
- With Cleo, SAP EDI Integration is Easy
- Benefits of pre-built integration for SAP EDI include:
- Cleo's Proven SAP EDI Solution
What Is SAP EDI?
For starters, EDI is a widely used method for automating the exchange of business records and documents in a standard electronic format between applications within a system. No special arrangements are needed, making it easy for business partners to share technical documents seamlessly. Notably, even SAP supports the creation of EDI files through Application Link Enabling (ALE), facilitating the exchange of business data among various systems within the SAP framework.
So what does EDI have to do with SAP? When an organization uses SAP, EDI will exchange business documents from the host organization's SAP ERP, with the system of an external partner. Therefore allowing the two parties to efficiently communicate using automation.
Does SAP Offer EDI?
In short, yes. Among several architectures and EDI tools, SAP EDI enables the electronic exchange of business transactions across applications. Providing a certain level of EDI capability. For example, using Intermediate Documents (IDOCs) for key tasks:
- Messaging: EDI conveys outbound messages, like order confirmations.
- Reception: It receives inbound messages, such as sales, via the EDI system.
- Conversion: The EDI converter changes IDOCs to the EDI format.
This digital approach replaces older methods, making document sharing between companies more efficient.
What Is SAP's IDoc Interface?
Intermediate documents (IDocs) are an SAP vessel that takes the data of a business transaction from one platform or system to another, in the form of an electronic message. The transfer can be performed between internal systems or to an external system. IDocs are a mature technology, ubiquitously in place around the world, and are a reliable method of communication that replaced less secure methods such as couriers, fax, or emails.
Additionally, the transfer from SAP to a non-SAP system is performed via EDI, whereas transfers between two SAP systems use application link enabling (ALE).
Usage of EDI for SAP customers
SAP customers often find the need to integrate EDI into their ERP systems to handle electronic purchase orders, advanced shipment notifications, and invoices. In the SAP ecosystem, EDI messages can be seamlessly mapped into IDocs and directly posted into SAP ERP or S/4HANA. This integration is commonly achieved through third-party EDI platforms or EDI services, such as VANs with SAP integrations, SAP's own products like SAP Process Orchestration, or SAP Cloud Platform integration. It's not uncommon for SAP users to directly read flat files from the SAP application server for purposes of the EDI process.
What Are SAP's Outbound and Inbound EDI Mapping Processes?
EDI mapping involves converting and adapting electronic business documents from one format to another. This enables smooth communication and data sharing between various trading partners or systems. The outbound process is for sending a message, while the inbound process is for receiving a message.
Outbound Process
The outbound process is for transmitting messages/data from an SAP system to an external system. This could be to a customer, trading partner, or any organization. The outbound process produces application document(s) and transforms them into a standard, intermediate record or document. Afterward, the intermediate document is transformed into an EDI standard document format that the recipient's system can understand. This EDI-formatted document is then sent to the recipient. Lastly, the recipient replies to the sender with a transmission status.
Inbound Process
The inbound process is for receiving information from an external system. This too could be a customer, trading partner, or any organization. The inbound process involves receiving an EDI document, producing a receipt of the document, and then transforming it into a standard, intermediate record or document. This intermediate document is then transformed into an application document that the SAP system can process.
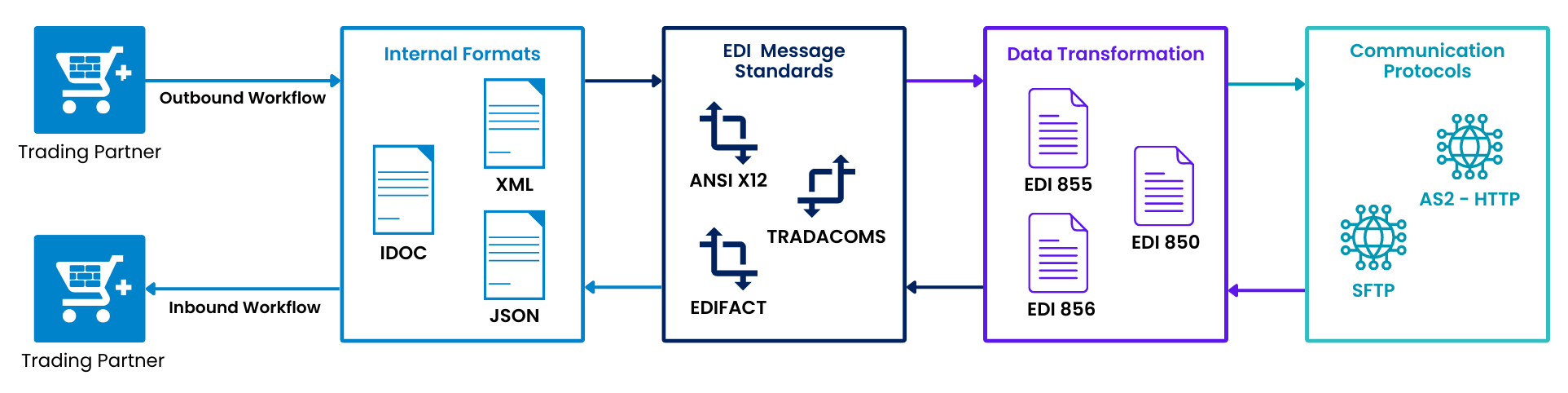
How Does EDI Work?
EDI is an essential part of many organizations that determines the efficiency of critical revenue-generating business processes
First off, both the sender and receiver of EDI messages will need the technology in place (e.g SAP/ERP or other EDI interface) to receive, generate, and process the electronic messages. The sender and receiver will likely be using different application programs to transmit messages. Therefore, the programs must be able to transform the messages into a standardized format that can be understood by both parties. This can be done by agreeing on a communication standard and then implementing an EDI translator. Popular standard formats include ANSI X12 and UN/EDIFACT. For reference, UN/EDIFACT is short for United Nations rules for Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport, and is a set of internationally standardized communication guidelines for exchanged data tags and message formats between computer systems in different networks. To actually send a message, the sender will create a message that includes the information they wish to communicate. They will then send the message through the translator system.
- The EDI translator then transforms the message type into a universally accepted format that is easily read by any system. For example, as we mentioned above, this could be EDIFACT or ANSI X12.
- The message, which is now in a standard format, is then sent to the recipient's translator via the internet, VPN, WAN, or a different channel.
- The recipient's translator then translates the standardized message into a different format that their application program can understand.
- The newly translated message is then sent to the receiver's application program, which is then processed by posting in the ERP.
- The receiver's application program then interprets the translated message.
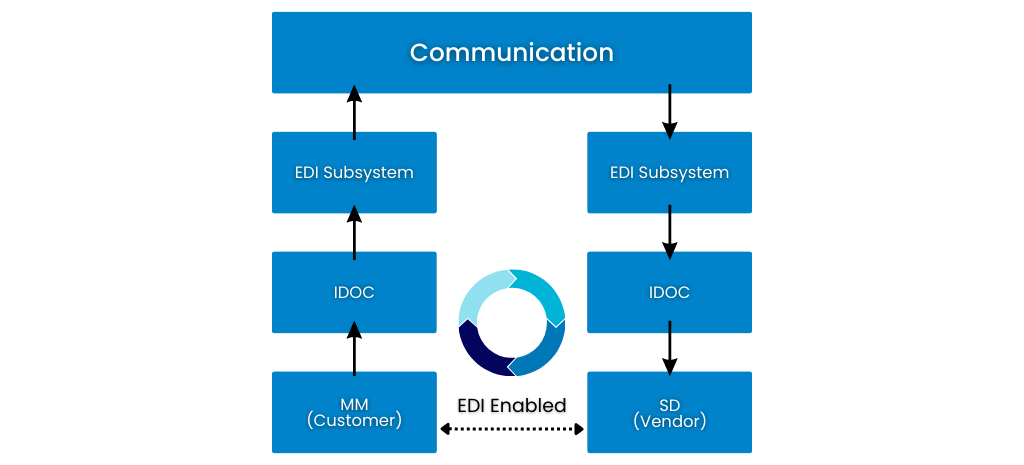
SAP EDI Architecture
There are three key aspects of SAP EDI architecture. These include:
- EDI-Enabled Applications: Automates communication and transactions between two systems or parties for EDI order processing.
- The IDoc Interface: An open interface, meaning a public standard for connecting hardware to hardware and software to software. Also possesses the capabilities to structure the application's interface.
- The EDI Subsystem: Transforms the IDocs into EDI formats and vice-versa. Then, either sends/receives the EDI message to or from the trading partner. Note: EDI subsystems are not provided within the SAP system. Therefore, customers must find an outside EDI system solution to implement.
Should You Use SAP's EDI or a Separate EDI Solution?
Deciding whether to use a SAP EDI or a separate EDI integration solution depends on the needs of your business, how important innovation is when it comes to operations, and personal preference. Below we identify the advantages and disadvantages of using SAP's EDI solution.
Pros of SAP EDI
- Increases efficiency and reliability by removing manual intervention.
- Shorten processing time by automating internal and B2B communication between systems and organizations.
- Digitalizes the processing and storing of data.
- Minimizes errors regarding data entry and pulling data.
- Reduces costs associated with paper, printer ink, admin machines (fax, printer, etc.), postage fees, human labor, etc.
- Improves inventory management by offering quick communication responses and minimizes processing errors, manual intervention, transaction cost, etc.
Cons of SAP EDI
- Does not provide an EDI subsystem, meaning you need a separate solution to transform IDocs into EDI formats and vice-versa.
- Reliance on one solution for both ERP and EDI increases the likelihood of system-wide downtime and EDI issues.
- Integration stretches beyond ERPs and EDI; for example, businesses may want to integrate TMSs, WMSs, CRMs, and/or eCommerce solutions into their digital ecosystem.
- The solution may experience less innovation due to EDI not being SAP's main area of focus.
For additional context on why your ERP platform shouldn't also handle EDI, check out our blog.
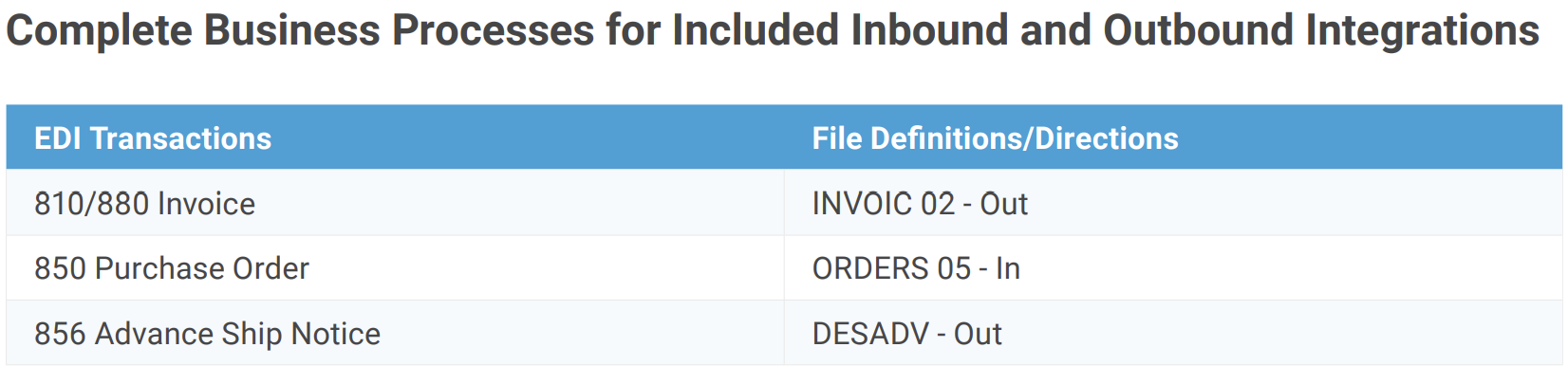
Common SAP EDI Transaction Codes
Among many EDI codes, the most common EDI transactions used in SAP are shown below to achieve complete business processes for inbound and outbound workflows. Followed by a more extensive list of transactions to be EDI compliant, depending on system and partner.
Some additionally used SAP EDI transaction codes include:
• EDI 820: Payment Order/Remittance Advice
• EDI 831: Application Control Totals
• EDI 832: Price/Sales Catalog
• EDI 836: Procurement Notices
• EDI 838: Trading Partner Profile
• EDI 839: Project Cost Reporting
• EDI 840: Request for Quotation
• EDI 841: Specifications/Technical Information
• EDI 842: Nonconformance Report
• EDI 843: Response to Request for Quotation
• EDI 845: Price Authorization Acknowledgment/Status
• EDI 846: Inventory Inquiry/Advice
• EDI 847: Material Claim
• EDI 848: Material Safety Data Sheet
• EDI 849: Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment
• EDI 850: Purchase Order
• EDI 851: Asset Schedule
• EDI 852: Product Activity Data
• EDI 853: Routing and Carrier Instruction
• EDI 855: Purchase Order Acknowledgment
• EDI 856: Ship Notice/Manifest
• EDI 857: Shipment and Billing Notice
• EDI 860: Purchase Order Change Request: Buyer Initiated
• EDI 861: Receiving Advice/Acceptance Certificate
• EDI 862: Shipping Schedule
• EDI 863: Report of Test Results
• EDI 864: Text Message
• EDI 865: Purchase Order Change Acknowledgment/Request: Seller Initiated
• EDI 866: Production Sequence
• EDI 867: Product Transfer and Resale Report
• EDI 869: Order Status Inquiry
• EDI 870: Order Status Report
• EDI 888: Item Maintenance
• EDI 893: Item Information Request
• EDI 894: Delivery/Return Base Record
• EDI 895: Delivery/Return Acknowledgment or Adjustment
• EDI 896: Product Dimension Maintenance
• EDI 940: Warehouse Shipping Order
• EDI 943: Warehouse Stock Transfer Shipment Advice
• EDI 944: Warehouse Stock Transfer Receipt Advice
• EDI 945: Warehouse Shipping Advice
• EDI 947: Warehouse Inventory Adjustment Advice
• EDI 980: Functional Group Totals
• EDI 997: Functional Acknowledgment
• EDI 998: Set Cancellation
• EDI 999: Implementation Acknowledgment
EDI Integration in SAP
You can integrate an EDI solution with SAP by following two main steps:
Step 1: Map EDI to SAP IDoc
First, build a map between the inbound EDI to SAP IDoc. You will only need to do this once, as all future transactions will use this map, the schema, and the rules you set up.
Step 2: Deliver the IDoc to SAP via Orchestration
Next, create an SAP process orchestration that enables inbound EDI messages to be received by SAP. From here, communication will be automated via EDI, ensuring efficient communication between both systems involved.
With Cleo, SAP EDI Integration is Easy
SAP EDI integration does not have to be complex. With Cleo, we simplified the process so your business can get up in running with minimal effort, time, and resources; speeding time to revenue.

Brother trusted Cleo to manage their EDI while upgrading to SAP S/4HANA
Managed Services approach helps strengthen revenue-critical processes through B2B, D2C relationships, while improving SLA compliance
A Dedicated Integration Connector for SAP
While certain EDI providers offer different solutions ranging in complexity, one of the ways Cleo simplifies the SAP EDI integration process is with our SAP ERP integration connector. Our ERP connector for SAP includes a large collection of resources, such as customizable rulesets, business processes, source and target schemas, and source and target adapters.
These customizable pre-built templates allow your business to edit them until they fit the requirements of your business, as well as your trading partners' requirements. This improves onboarding efficiency by:
- Eliminating custom-coding, so you can onboard new trading partners at unparalleled speeds.
- Minimizing errors by removing human intervention, and instead harnessing automation to process inbound and outbound EDI transactions between external trading partners and your SAP ERP.
We also offer sample data and file structures that can be used for EDI testing. Furthermore, we provide a metadata importer, which uses the IDoc definitions to generate flat file schemas that represent the SAP-side interface in rulesets, for both source and target cases.
Upon deployment of the SAP connector, customized versions of these integrations automate processes that connect your SAP system with external trading partners.
The IDoc interface is used for sending and receiving outbound and inbound transactions via the file system. This ERP connector delivers a centralized, SAP-certified configuration and control solution for all communications and data integration activity, allowing you to:
- Import SAP-specific metadata and generate corresponding schemas
- Deliver EDI order-to-cash and procure-to-pay transactions by customizing the included sample integration projects.
- Create custom business integration projects for other transaction types, from scratch.
- Track EDI and IDoc transactions using an SAP Dashboard report.
Overall, our connector delivers reliable integration with SAP, and all other business-critical systems, providing a complete and unified view of customer engagement throughout all business processes.
Cleo's Pre-Built Supply Chain Integration for SAP S/4HANA
Another tool Cleo offers to improve efficiency is our pre-built supply chain integration for SAP S/4HANA. It ushers faster time-to-market by quickly connecting a system of record (e.g. ERP, TMS, or WMS) with SAP.
Our pre-built supply chain integration comes with out-of-the-box API and EDI integrations, along with pre-built schemas, rulesets, business processes, and other resources used for accelerating the development, deployment/execution, and testing of integrations.
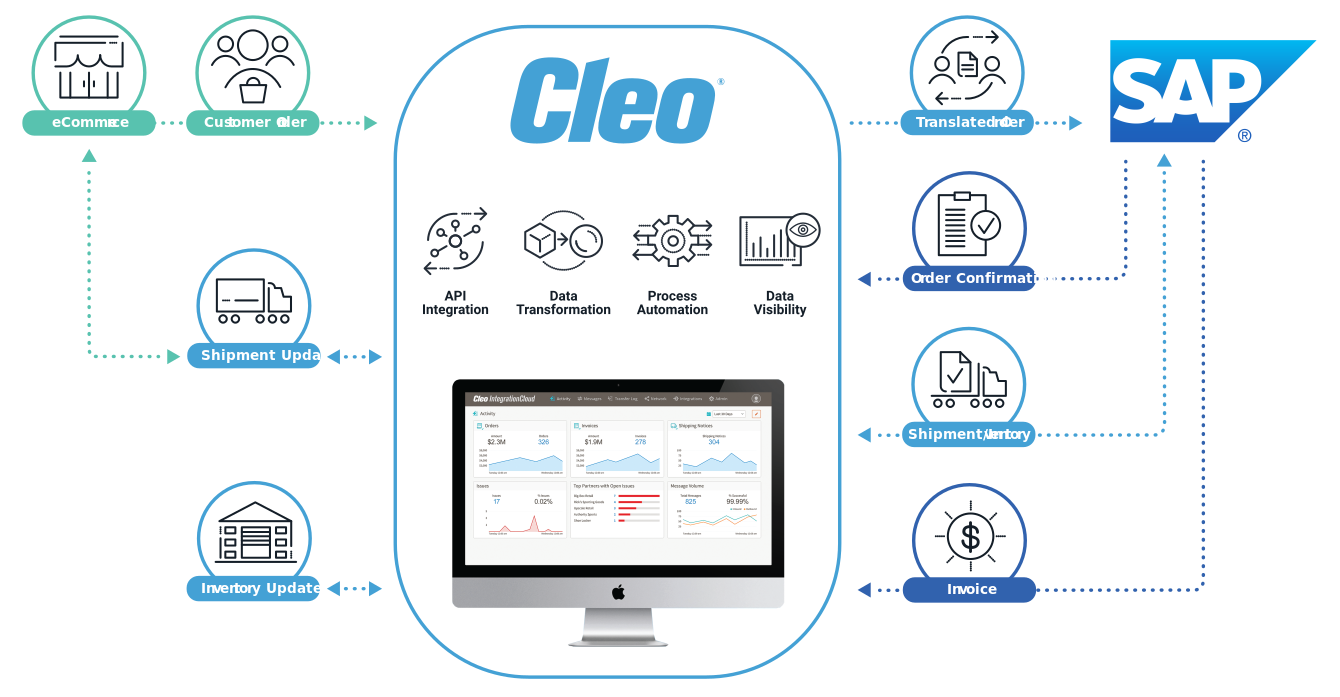
Benefits of pre-built integration for SAP EDI include:
Create Fluid Digital Business Process Flows:
- Streamline X12 EDI processing and exchange between external trade partners and your SAP system.
- Swiftly construct sturdy, tailor-made integrations with clients, suppliers, and other business associates.
Simplify SAP Integration Complexity:
- Streamline SAP integration, contrasting with conventional application integration methods or mapping libraries.
- Access comprehensive, customizable templates for typical order-to-cash transactions.
- Seamlessly coordinate process dynamics, source and target documents, mapping, adapters, and integration elements.
Revitalize Your SAP Integration:
- Break free from outdated, overlapping mapping samples sourced from consulting projects.
- Depend on finely tuned predefined templates that surpass your most prevalent SAP integration requisites.
Incorporate SAP IDoc Interface Files:
- Harness the metadata importer employing SAP-exported IDoc definitions.
- Generate document definitions representing SAP's data interface, for use as source or target schemas in rulesets.
Minimize Errors and Cycle Time:
- Automate the exchange and handling of electronic transactions.
- Preconfigured elements detect and automate inbound and outbound EDI transaction processing.
- Handle partner integration through exception management to safeguard vital performance SLAs.
Instantly Sample Data and Precedents:
- Test and perfect your EDI integrations via sample inbound and outbound EDI and IDoc data and file structures for SAP.
- Conveniently assess your SAP business processes locally, verifying integration execution status and troubleshooting exceptions.
The Only SAP Integration Solution You Need
Cleo's Proven SAP EDI Solution
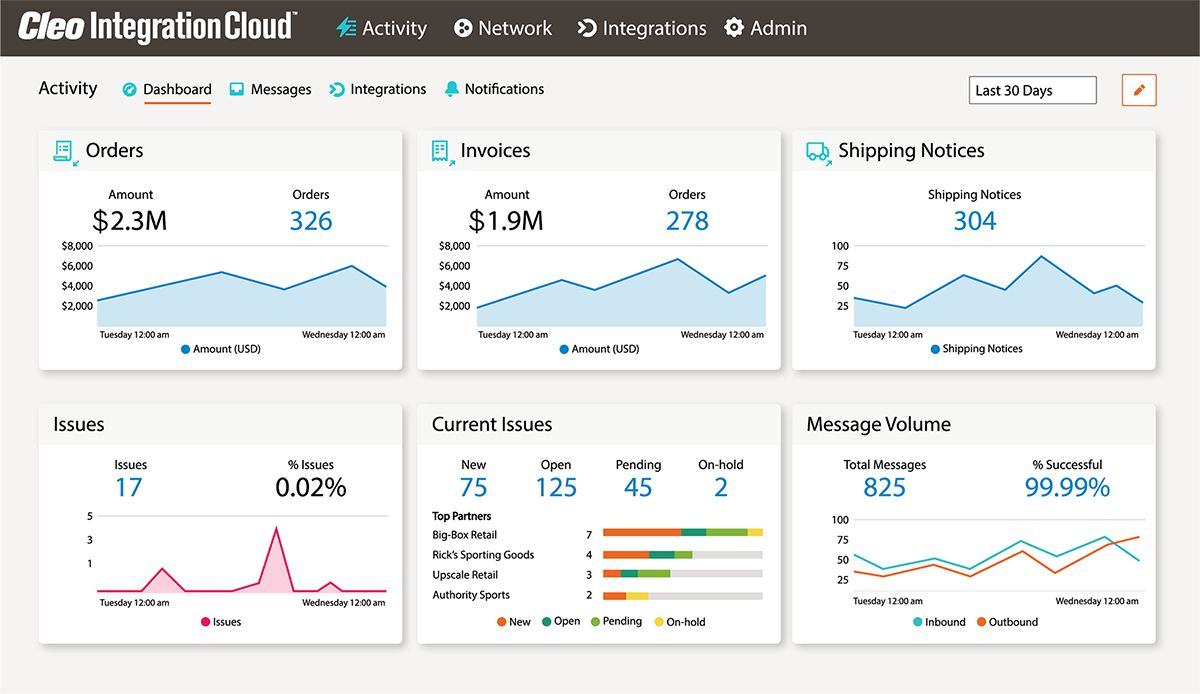
On top of our SAP integration connector and pre-built supply chain integration for SAP, Cleo offers a comprehensive EDI solution, Cleo Integration Cloud (CIC). CIC can fully integrate your digital ecosystem (both with internal and external systems) while providing the following benefits:
● Business process automation.
● Rapid trading partner onboarding.
● Quick error resolution.
● Real-time updates and data sharing.
● Flexible service offerings: self-service, managed services, or blended services.
● End-to-end EDI integration visibility.
● API-based integration.
● Platform scalability.
● User-friendly design.
● A wide variety of protocol support,
● …and more.
If your company is looking for a SAP cloud EDI integration solution, you are in the hands of true professionals. Our dynamic team of technical experts that possess more than 900+ years of combined integration experience, along with our resourceful and knowledgeable business team members, lead the way in implementing, customizing, and integrating ERP solutions, including SAP.
At Cleo, we closely collaborate with our customers to transition their business processes to our innovative cloud platform, offering complete ERP integration solutions, and delivering unparalleled levels of productivity and efficiency through their digital business. We are here to help answer any questions you may encounter throughout the implementation, and provide customers with a ticketing system, training videos/courses, live workshops, written guides and educational resources, and more—to ensure your SAP EDI integration goes off without a hitch.
Contact us today at sales@cleo.com or +1.815.282.7695 to leverage our expertise and start experiencing the advantages of EDI integration with world-class EDI software. And be sure to explore some of our educational resources through our resource library.

Simplify Your SAP S/4HANA EDI Integration
Join thousands of organizations seamlessly integrating EDI with SAP S/4HANA.

About Cleo
Instantly access demo videos

Comprehensive Guide to Gaining B2B Control

Duraflame Case Study