What the Modern Enterprise Should Know About B2B Integration
Well before businesses ever start selling, transacting, and doing business with their customers, they must sell, transact, and do business with other businesses. The need to digitally connect and communicate quickly and reliably with other organizations – retailers, manufacturers, shippers, etc. – is why business-to-business (B2B) integration technologies are increasingly in demand.
While it’s important to facilitate these critical data exchange requirements through modern business and system integration strategies, B2B is also very difficult to do, which is why so many companies use cloud managed services for their specialized B2B integration software. Before deciding on a solution, however, it’s important for the enterprise to first understand all that B2B integration entails, the direction B2B integration technologies are headed, and how they can improve their revenue-driving business processes using these solutions.
What is B2B Integration?
B2B (Business-to-business) integration is the process of connecting and automating business processes between two or more companies, allowing them to streamline supply chain operations, reduce manual errors, and improve efficiency and collaboration with their trading partners. The process involves the exchange of electronic data, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipment notifications, between the systems of different organizations.
In short, B2B integration is a comprehensive digital strategy that enables business process automation and the foundation for businesses to integrate major applications.
Today’s global business ecosystem requires companies to connect, communicate, and collaborate with:
- Customers
- Partners
- Suppliers
- Service vendors
So why do we need B2B integration? For one, every organization takes its own approach to exchanging files and messages with its trading partners. That means each business uses a distinct mix of systems, cloud, and applications that require various formats, B2B protocols, and security and governance considerations. B2B integration helps these disparate technologies – which don’t inherently communicate with each other – communicate and seamlessly exchange business-critical information within and across business lines.
The ultimate goal of B2B integration, then, is to improve external logistic workflows and system integration throughout the supply chain and the value chain. But B2B integration also sets the table for end-to-end process execution – including business process management (BPM), supply chain visibility, and global community management – for comprehensive control of your important business data exchanges.
What is a B2B Integration Platform?
A B2B integration platform enables businesses to integrate all their intricate B2B and electronic data interchange (EDI) operations across their organization and partner network. The platform gathers information from source apps, converts it into standardized forms, and then sends the documents to the business partner via the proper transport protocol. B2B integration software can be implemented through hosted cloud or on-premises B2B integration services.
How Does B2B Integration Work?
B2B integration can be achieved through a variety of technologies and standards, such as EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), API (Application Programming Interface), and web services. Business integration starts with pulling information from an internal source application and transferring it to an end external application via a secure data movement and integration platform. The nature of technology today means that one or both of these applications could be cloud-based, on-premise, or hybrid – a combination of both. Furthermore, B2B services and platform providers must also support cloud integration and hybrid integration scenarios.
Here are the four components of a standard B2B integration process.
No. 1: Source Application
B2B integration begins by extracting information out of your front-end business application. This document could be a purchase order (PO) from your ERP system or a specific retail store’s monthly sales figures from a point-of-sale (POS) system. How the data gets pulled out, however, depends on the application itself, whether it’s a SaaS solution or is deployed on servers behind your own firewall.
Some software solutions provide APIs for this step, and some use traditional middleware technology. But a modern B2B integration solution should be able to flexibly connect to the application through whatever method it allows, so it can begin preparing the data to be transmitted to the external business partner.
No. 2: Data Format
The part about technologies not natively communicating with each other is never more evident than in the payload format. That’s because not all data is standardized. Business systems and applications produce and store information in their own proprietary formats (iDoc or flat file, for instance), which usually must be converted into EDI, XML, CSV, JSON, and other standardized formats to allow for integration into an ERP, TMS, CRM, or another enterprise system of record.
Many industries also require their own specific formats, and even those could vary depending on their location. Global companies who source materials and transact with geo-located retailers, distributors, and logistics organizations require support for a breadth of data formats so the target application can automatically ingest it and data can keep flowing efficiently. It’s why data transformation and mapping is so critical in a B2B integration solution.
No. 3: Transport Protocol
Much like a CB, walkie-talkie, or other radio communication device, both parties must agree on a communication channel, or protocol, to exchange information. A trading partner (and even industry) most often will dictate the transport mechanism, but determining how to send a message (in the proper format, over the internet) ultimately requires an assessment of the payload:
Does it contain sensitive information?
Do you need confirmation that it was received?
How big is the file?
How fast does it have to get there?
From AS2, SFTP, HTTPs, Web Services, and even proprietary high-speed file transfer methods, there are a number of advanced protocols out there to facilitate data exchange. But companies using B2B integration solutions that support any protocol are more agile and more business-friendly.
No. 4: Target Application
The final step in a B2B integration involves the target application, in which your trading partner receives and processes the data sent making it readable and able to be integrated into their core business systems. The target application must then be able to reliably transform the data from the original standardized format back into one that’s accessible and ingested throughout the ecosystem. Many organizations offer web portals for easier uploading and exchange and also to automatically execute the transformation process and application ingestion.
For years, business communications were human-oriented; things like fax and email were the primary means of exchanging business data. But through consistent modernization efforts, pushed by the increasing emphasis on digital automation along with evolving B2B integration patterns – and the various components needed to accommodate them – it’s easy to see that enterprises are rapidly adapting and enhancing their approach to B2B in order to keep up with the speed of modern business.
Today, these four components are delivered by a B2B integration platform that collects data from source applications, transforms it into the proper format, and delivers it to the target application using the appropriate transport mechanism. In doing so, the platform also serves two key types of integration.
2 Types of B2B Integration
There are two key types of B2B integration: data-level integration and people-level integration. We’ve mostly talked about data-level at this point, but it’s also critically important to consider the human role of integration.
Data-Level Integration
Data-level integration is the automated document exchange between external applications, which could include all transactions in an order-to-cash or load-tender-to-invoice process, for example. Integrating at this level requires a high degree of automation for connecting using a secure protocol, for the electronic exchange of data, and for the data transformation processes that convert documents into a format readable by each trading partner’s application.
People-Level Integration
People-level integration enables B2B collaboration among people in different companies during business processes, such as dispute resolution, trading partner onboarding, and other customer support scenarios. This level of integration demands various trading partner management capabilities to manage profiles (and enable your partners to do it themselves) and also capture and share data related to performance. People-level integration solutions enabling traceability and audit control come in handy for improved relationship management, including dispute resolution, chargeback situations, any missed SLAs, and other issues that require heavy collaboration.
B2B Integration Example in Real Life
A retail order-to-cash scenario reflects typical B2B integration concepts. A big-box retailer like Walmart looking to buy cereal from Kellogg’s creates an EDI data flow looks like this:
- Walmart preps an order in its ERP or purchasing system. The order is pulled out and translated into an EDI document: an 850 Purchase Order.
- The 850 is then securely transmitted to Kellogg’s via the internet (over AS2, for instance) and processed by Kellogg’s.
- Kellogg’s sends back a 997 Functional Acknowledgement (and/or an 855 EDI Purchase Order Acknowledgement to provide fulfillment status) to confirm the order was received.
- After processing the order, Kellogg’s sends an 856 Advance Shipping Notice over the same AS2 connection to let Walmart know what’s coming.
- Walmart receives the 856, sends a 997, and then integrates the 856 into its back-end ERP and prepares to receive shipment.
- Once Kellogg’s ships the order, it sends an 810 Invoice is sent to Walmart and Walmart returns a 997.
- Walmart sends an 820 Payment Order to Kellogg’s to confirm payment details, and another 997 goes back to Walmart to acknowledge document receipt.
This simple order kicks off additional B2B integration processes for both buyer and seller, including converting an 850 into a 940 Warehouse Shipping Order, and leverages the same data movement and transformation capabilities to electronically communicate with other distribution, warehousing, and fulfillment applications.
The Challenges with Existing B2B Integration Technology
Traditional B2B integration platforms like VANs and homegrown solutions are slow, inflexible, and typically expensive to maintain, and alternatives like iPaaS solutions are mainly focused on solving developer-level API-based integration problems. There also are a ton of B2B integration vendors out there that can deliver a fair amount of useful technology, but most can’t support every modern format, protocol, or governance need to meet EDI B2B integration and other business integration requirements.
But the heavy lifting of today’s B2B communications requires a more modern approach that goes beyond integration “tools” that are fit for purpose. Today’s enterprises have a greater thirst for how their critical data flows fit into the broader context of the business, and they demand an experience that helps connect how these specialized B2B processes drive overall business revenue and goals.
But most existing B2B integration technologies can’t deliver the experience customers are seeking and actually create more obstacles to adoption. On that note, here are the 10 main challenges most businesses face in trying to solve B2B integration with deficient technology today:
- It’s intimidating
- It’s inefficient
- It lacks business content
- It lacks business context
- It’s opaque
- It offers limited business controls
- It has weak collaboration features
- It gives inadequate business insights
- It facilitates poor interactions
- It lacks personalized content
If vendors could plug these gaps, more organizations could improve their B2B integration processes and gain quantifiable outcomes oriented to the business.
How Companies Benefit from Improved B2B Integration
Because the need for B2B integration is so ubiquitous, an organization’s industry, size, or location will not exclude anyone from reaping the benefits of B2B integration.
Benefits by Industry
- Financial services: B2B integration technology connects numerous banks and brokerages while providing the robust security, governance, and audit trail capabilities, as well as the real-time visibility, required to deliver expanded banking services to customers.
- Healthcare: Securely connecting hospitals, labs, doctor’s offices, insurance providers, and other medical-type facilities is no easy task. A modern B2B integration solution can replace a VAN and automate EDI-heavy insurance enrollments, eligibility, authorizations, claims, and payment processes.
- Logistics: High-volume logistics organizations use B2B integration to ensure the accurate and timely delivery of everything from purchase orders to shipment confirmations to advance ship notices and also to integrate with warehouse management systems.
- Manufacturing: What if you could exchange customer and supplier information over various SFTP connections, use AS2 to securely communicate with your bank, and ingest engineering files right into SAP? B2B integration supports various workflow scenarios and file transfer methods.
- Retail: Automate the conversion of X12 documents to an XML format your ERP application can handle and reduce chargebacks, time, and fees.
- Software and technology: Cloud and SaaS organizations must integrate with a lot of customers and handle massive data volumes. A B2B integration platform does all the heavy data lifting so tech companies maintain 100% uptime and never miss an SLA.
Additional Benefits
In addition to the automation, multi-protocol support, and application integration benefits, organizations deploying a robust B2B integration platform also gain:
- Improved partner onboarding: Reduce manual processes, bring on new customers faster, and increase team productivity
- Expanded governance: Ensure the secure integration of your data, and meet stringent government and industry compliance regulations.
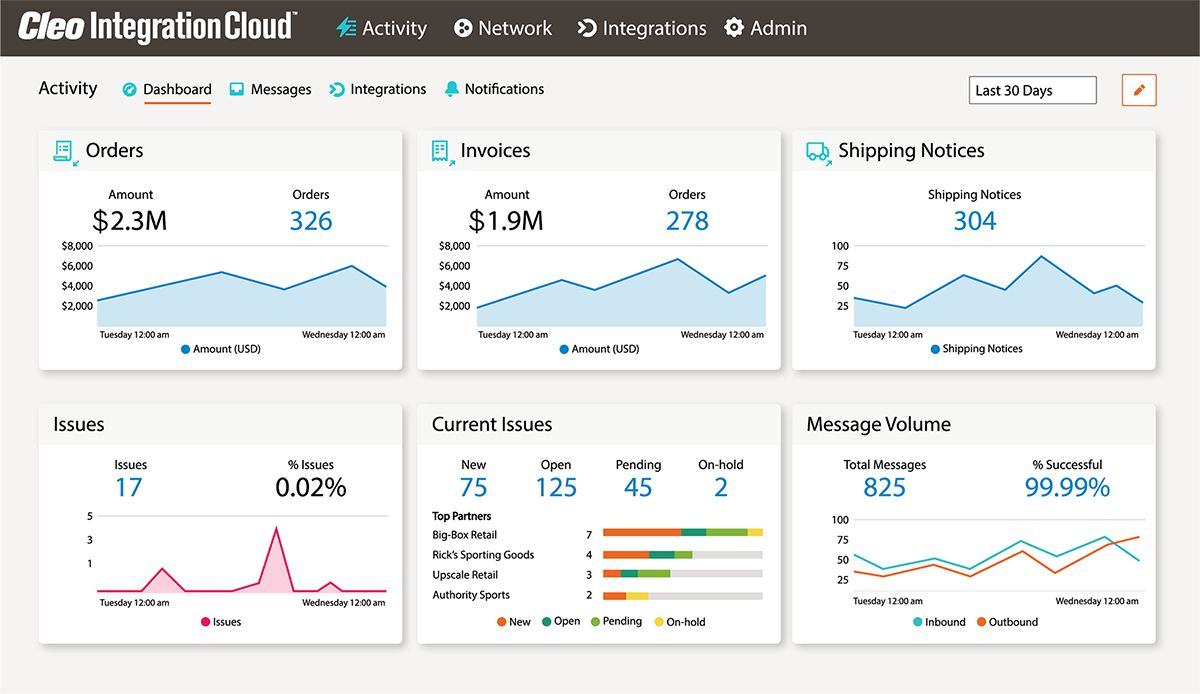
- Comprehensive visibility: A centralized view of revenue-driving B2B processes provides actionable intelligence to the enterprise, enabling more responsiveness and better customer service.
How As-a-Service Solutions Improve B2B Integration
Businesses require a reliable and agile way to enable electronic interactions between organizations and their ecosystem, but managing these B2B systems and the specialized talent to run them is a challenge most organizations are no longer willing to take on.
Modern B2B integration involves a technology approach that combines software and integration expertise to provide organizations a frictionless way to achieve their B2B integration needs. An ecosystem-driven cloud integration strategy built for the cloud-first organization, flexible B2B integration is a more comprehensive alternative to the traditional cloud managed services offerings that fail to deliver on the B2B expertise, the robust capabilities, and the visibility companies demand.
This style of B2B integration puts the complexities of data processes like EDI – including owning and maintaining complex software, infrastructure, processes, and talent – into the hands of the experts while giving companies visibility into the process to monitor and act on critical B2B communications as needed. It’s all the robust data movement and data transformation capabilities underneath, and all the visibility, governance, and collaboration on the surface, tied neatly together via a single platform.
Choosing a B2B Integration Platform
Evaluating and comparing B2B integration solution platforms is a time consuming (yet worthwhile) undertaking. The right platform will empower internal teams with the greater visibility, flexibility and faster onboarding that will also in turn create a better customer experience for the businesses you regularly exchange data with. This ungated ultimate guide: Choosing a Cloud Data Integration Platform walks you through current trends in integration technology, provides up-to-date platform comparisons, and lays out a strategy for evaluating your current solution.
The Future of B2B Integration
The time and resources organizations will be able to devote to their complex yet critical B2B integration processes will continue to diminish, and businesses will further seek to hand the heavy B2B lifting off to seasoned integration professionals.
The enterprise of the future will no longer struggle to facilitate frictionless, fluid interactions with its most important business partners. It will no longer have to prolong time to value in adding new business because it can’t support a customer’s requested data format or protocol. It will no longer lack critical business intelligence – gone is the guesswork of how to interpret reports and dashboard data surrounding key revenue-driving business processes.
And thus, the future of B2B integration is more than just technology; it’s an intuitive, self-service experience that reliably executes the critical data exchanges and enables real-time interaction and business agility. The future of B2B integration also encompasses the confidence in knowing that you cannot connect anytime, anywhere and do business faster and better than the competition.
Why Cleo Integration Cloud
Cleo Integration Cloud combines service and technology to provide the most flexible and frictionless way to exchange B2B data. A cutting-edge ecosystem-driven cloud integration platform focused on creating value at the edges of business networks, Cleo Integration Cloud shields organizations from the complexities of multi-enterprise and application integration, and further enables the real-time visibility and governance required to gain insight and control across important partner and customer relationships.

About Cleo