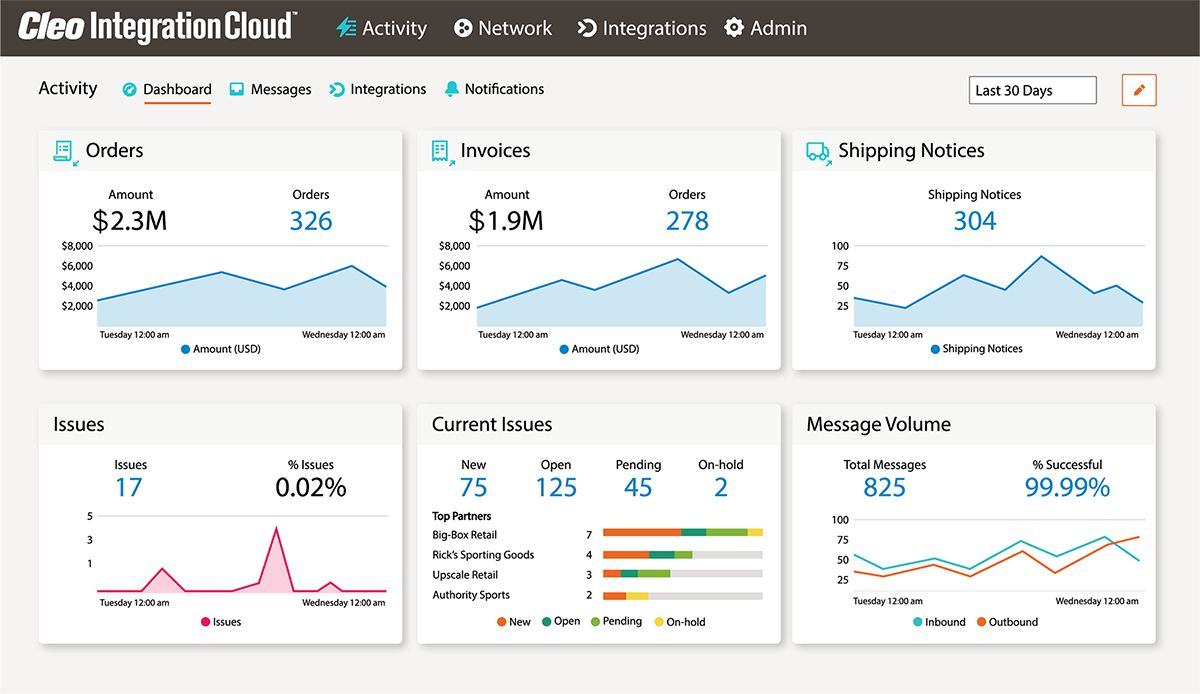
How EDI in Transportation and Logistics Works

Companies with a structured and sophisticated logistics strategy that includes EDI logistics software can do all kinds of incredible things - improve operational efficiency, increase visibility into their supply chain, and most of all, strengthen customer relationships throughout their ecosystem.
In order to accomplish that, however, companies need to first have the proper EDI software in place. EDI remains the standard for electronic transactions between businesses, and that is no exception in the logistics industry.
What is EDI in Logistics?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a standardized data format protocol that adds communication efficiency between businesses and avoids human error in the process. Before EDI, it was usual practice to manually extract data from one system, record it on paper or a spreadsheet, send it to the correct recipient, and then manually enter it into the recipient system. This method not only took a lot of time, but was prone to challenges brought on by human error.
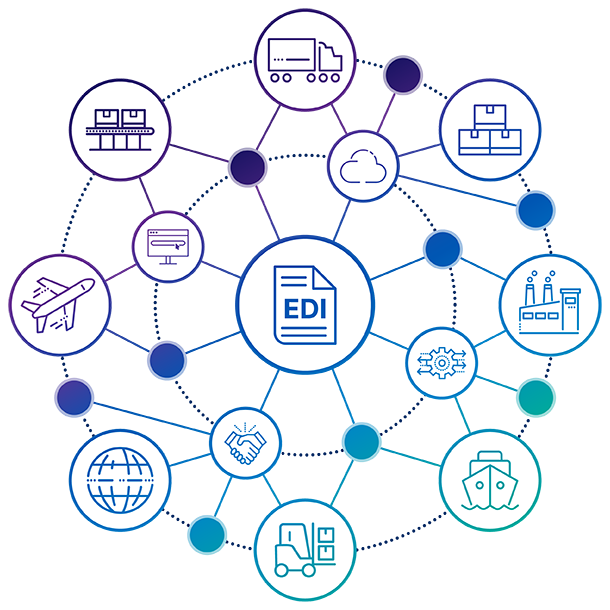
How Does EDI for Logistics Work?
Logistics organizations rely on EDI data to simply get things done. Whether that is onboarding a new trading partner, communicating with a customer, or receiving an EDI load tender, the bottom line is logistics companies have needed an efficient EDI logistics software strategy for decades and will continue to for years to come.
Since the late 1960s, organizations involved in the global supply chain have been using EDI tools. For example, today's biggest trucking companies, like FedEx, UPS, XPO Logistics, etc., all employ EDI to speed up document transfers and B2B communication, resulting in lower costs and delays, better data accuracy, and increased customer satisfaction.
Connecting and integrating EDI transport data across a multi-enterprise supply chain is of the utmost importance. Modernized EDI logistics software can extend data flows to integrate into core applications to expand a company's online presence through seamless eCommerce and marketplace integration.
Scaling quickly is what every logistics company across the globe wants to be able to do. Modernized EDI systems give organizations the control that they require to conduct business with customers and trading partners. Those critical data exchanges between businesses must be standardized, automated, integrated sufficiently, and simplified. Without those four key ingredients, logistics companies are going to struggle.
The Logistics of EDI
Along with the supply chain, EDI has often been referred to as the lifeblood of the logistics industry. From all of the EDI communication standards to the various EDI messages, the critical data communication standard that is EDI has been fundamental throughout the logistics industry for a long time.
As much as any other industry, if not more, logistics companies must be able to scale - and scale quickly. Companies need to handle the sending and receiving of electronic documents, such as X12, EDIFACT, Tradacoms, ODETTE, EANCOM, HIPAA, VDA, and much more. Throughout the logistics industry, becoming EDI capable means not just being able to accommodate and leverage all of these communication standards, but to do so efficiently and fast.
EDI's primary goal is designed to make the workflow of a logistics company smooth and easier through the standardization, automation, integration, and simplification of those critical data exchanges. But that's why it takes the right solution to make these things possible, and the right solution begins with modernizing your EDI.

Conquer Logistics Integration Challenges
Move and transform any data to seamlessly integrate with any partner and application. Dive deeper and learn how our solution can transform your operations.
Common EDI Logistics Transactions
Every industry, from transportation and logistics to manufacturing or retail has its own recurring EDI transactions that they will need to not just familiarize themselves with, but learn to master and know the ins and outs of. Each EDI document transaction contains a certain amount of important data, and without it, the EDI document is practically useless.
EDI formatting must be adhered to based on strict formatting rules that define how and where each part of data on the document is found and utilized. Each EDI document is assigned one of several transaction numbers from the EDI public format. This allows logistics companies to streamline EDI transport transactions and improve EDI order processing using efficient EDI integration and the seamless automation of B2B workflows between both internal and external systems, applications, and cloud ecosystems.
Some of the most common EDI transport transactions for logistics companies include:
EDI 104: Air Shipment Information
EDI 106: Motor Carrier Rate Proposal
EDI 107: Request for Motor Carrier Rate Proposal
EDI 108: Response to a Motor Carrier Rate Proposal
EDI 109: Vessel Content Details
EDI 110: Air Freight Details and Invoice
EDI 120: Vehicle Shipping Order
EDI 121: Vehicle Service
EDI 125: Multilevel Railcar Load Details
EDI 126: Vehicle Application Advice
EDI 127: Vehicle Baying Order
EDI 128: Dealer Information
EDI 129: Vehicle Carrier Rate Update
EDI 160: Transportation Automatic Equipment Identification
EDI 161: Train Sheet
EDI 163: Transportation Appointment Schedule Information
EDI 204: Motor Carrier Load Tender
EDI 210: Motor Carrier Freight Details and Invoice
EDI 211: Motor Carrier Bill of Lading
EDI 212: Motor Carrier Delivery Trailer Manifest
EDI 213: Motor Carrier Shipment Status Inquiry
EDI 214: Transportation Carrier Ship. Status Message (e.g. truck or transport is delayed in customs)
EDI 215: Motor Carrier Pick-up Manifest
EDI 216: Motor Carrier Shipment Pick-up Notification
EDI 217: Motor Carrier Loading and Route Guide
EDI 219: Logistics Service Request
EDI 220: Logistics Service Response
EDI 222: Cartage Work Assignment
EDI 223: Consolidators Freight Bill and Invoice
EDI 224: Motor Carrier Summary Freight Bill Manifest
EDI 225: Response to a Cartage Work Assignment
EDI 227: Trailer Usage Report
EDI 228: Equipment Inspection Report
EDI 240: Motor Carrier Package Status
EDI 250: Purchase Order Shipment Management Document
EDI 300: Reservation (Booking Request) (Ocean)
EDI 301: Confirmation (Ocean)
EDI 303: Booking Cancellation (Ocean)
EDI 304: Shipping Instructions
EDI 309: Customs Manifest
EDI 310: Freight Receipt and Invoice (Ocean)
EDI 311: Canada Customs Information
EDI 312: Arrival Notice (Ocean)
EDI 313: Shipment Status Inquiry (Ocean)
EDI 315: Status Details (Ocean)
EDI 317: Delivery/Pickup Order
EDI 319: Terminal Information
EDI 322: Terminal Operations and Intermodal Ramp Activity
EDI 323: Vessel Schedule and Itinerary (Ocean)
EDI 324: Vessel Stow Plan (Ocean)
EDI 325: Consolidation of Goods in Container
EDI 326: Consignment Summary List
EDI 350: Customs Status Information
EDI 352: U.S. Customs Carrier General Order Status
EDI 353: Customs Events Advisory Details
EDI 354: U.S. Customs Auto. Manifest Archive Status
EDI 355: U.S. Customs Acceptance/Rejection
EDI 356: U.S. Customs Permit to Transfer Request
EDI 357: U.S. Customs In-Bond Information
EDI 358: Customs Consist Information
EDI 359: Customs Customer Profile Management
EDI 361: Carrier Interchange Agreement (Ocean)
EDI 404: Rail Carrier Shipment Information
EDI 410: Rail Carrier Freight Details and Invoice
EDI 412: Trailer or Container Repair Billing
EDI 414: Rail Carhire Settlements
EDI 417: Rail Carrier Waybill Interchange
EDI 418: Rail Advance Interchange Consist
EDI 419: Advance Car Disposition
EDI 420: Car Handling Information
EDI 421: Estimated Time of Arrival & Car Scheduling
EDI 422: Equipment Order
EDI 423: Rail Industrial Switch List
EDI 424: Rail Carrier Services Settlement
EDI 425: Rail Waybill Request
EDI 426: Rail Revenue Waybill
EDI 429: Railroad Retirement Activity
EDI 431: Railroad Station Master File
EDI 432: Rail Deprescription
EDI 433: Railroad Reciprocal Switch File
EDI 434: Railroad Mark Register Update Activity
EDI 435: Standard Transportation Commodity Code Master
EDI 436: Locomotive Information
EDI 437: Railroad Junctions & Interchanges Activity
EDI 440: Shipment Weights
EDI 451: Railroad Event Report
EDI 452: Railroad Problem Log Inquiry or Advice
EDI 453: Railroad Service Commitment Advice
EDI 455: Railroad Parameter Trace Registration
EDI 456: Railroad Equipment Inquiry or Advice
EDI 460: Railroad Price Distribution Request or Response
EDI 463: Rail Rate Reply
EDI 466: Rate Request
EDI 468: Rate Docket Journal Log
EDI 470: Railroad Clearance
EDI 475: Rail Route File Maintenance
EDI 485: Ratemaking Action
EDI 486: Rate Docket Expiration
EDI 490: Rate Group Definition
EDI 492: Miscellaneous Rates
EDI 494: Rail Scale Rates
EDI 601: U.S. Customs Export Shipment Information
EDI 603: Transportation Equipment Registration
EDI 715: Intermodal Group Loading Plan
EDI 854: Shipment Delivery Discrepancy Info.
EDI 858: Shipment Information
EDI 859: Freight Invoice
EDI 920: Loss or Damage Claim: Gen. Commodities
EDI 924: Loss or Damage Claim: Motor Vehicle
EDI 925: Claim Tracer
EDI 926: Claim Status Report and Tracer Reply
EDI 928: Automotive Inspection Detail
EDI 980: Functional Group Totals
EDI 990: Response to a Load Tender
EDI 998: Set Cancellation
Importance of EDI Compliance in Logistics
Logistics companies that aren't EDI-compliant are going to soon realize how quickly fines can add up. Going one step further, besides costing your company money, non-compliance impacts the trust companies have built with trading partners, jeopardizing those relationships and lowering the competitive threshold.
Logistics companies that aren't EDI-compliant are going to soon will readily realize how quickly fines can add up. In fact, recent survey data shows that poor integration overall led 14% of companies to lose $1 million or more in 2021, and nearly 1 in 4 lost $500,000 or more - not small sums for any business.
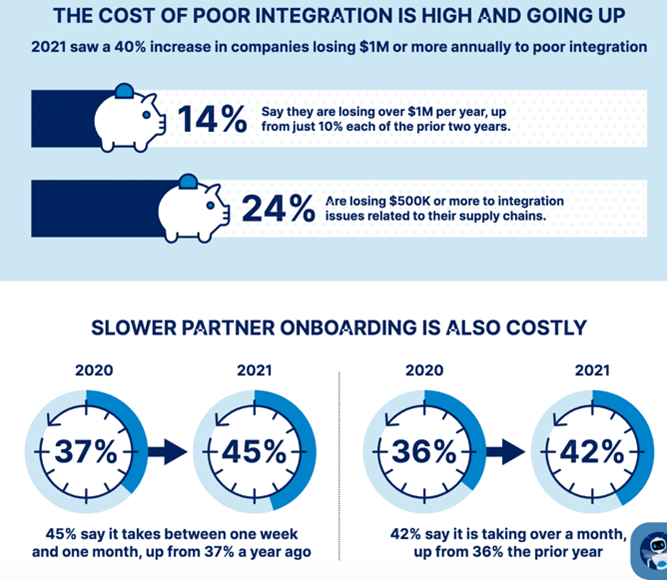
Going one step further, besides costing your company money, non-compliance impacts the trust companies have built with trading partners, jeopardizing those relationships and lowering the competitive threshold. Slow partner onboarding processes can often indicate trouble ahead unless integration technology is in place to get these revenue-driving relationships off on the right foot.
A modernized EDI interface means companies can stop worrying about missing their SLAs, eliminate the potential for inaccurate EDI, and ensure a fluid data process throughout a data lifecycle. Modern EDI tools can rapidly identify and address errors, pinpoint EDI compliance violations, and rapidly resolve any issues. Logistics companies can put an end to dropped, late, and inaccurate orders, and streamline end-to-end data transformation, orchestration, and integration with secure EDI.
Why Logistics Providers Should Think API + EDI
Alongside EDI, there is another integration approach that logistics providers can greatly benefit from; API integration. API integration utilizes APIs to digitize orders, load tenders, procurement processes, etc., to replace batch transactions (EDI). This way, logistics companies can obtain real-time API-enabled data flows that enhance and extend interactions between their ecosystem of manufacturers, retailers, and applications through integration.
A common misconception about API-based integration though is that it should replace EDI. However, this is not entirely true. Rather, API and EDI complement each other, operating best when working in tandem. The reason is that they each have their pros and cons.
Pros and Cons of API + EDI
API integration provides organizations with greater visibility, real-time processing, and live updates. These benefits are extremely beneficial for updating customers on where their order is in the supply chain, as well as helping logistics companies make more strategic decisions since they have access to more accurate data. However, API integrations require more resources to get up and running, they do not have industry-agreed-upon standards like EDI does, and each integration needs to be custom-built.
On the other hand, EDI integration is widely utilized by most larger organizations and trading partners, can process many files at once without experiencing system downtime, and is secure due to decades of use and advancements. However, EDI integration does not perform real-time processing, which means that real-time data and updates cannot be provided.
Consider an API + EDI Approach
Knowing what we discussed above, logistics providers may want to consider implementing an API + EDI approach. This way they can access the real-time data and updates that API integration supplies, while simultaneously achieving the security, stability, and greater processing power that EDI provides. Furthermore, an API + EDI approach gives logistics providers greater integration compatibility with trading partners since they are supporting more integration methods.

See Our Platform in Action
Watch a quick demo to learn how you can automate EDI & API, onboard parters faster, and directly integrate into any TMS/WMS.
API Use Cases for Logistics Providers
When it comes to specific API integration use cases for logistics providers, some of the most popular and useful ones include:
1. Real-Time Tracking
Logistics companies are using APIs to provide real-time tracking to their customers. By using APIs to share data between different players in their ecosystem, companies can provide customers with real-time updates on the status and location of their shipments, as well as optimize their operations by improving visibility and control over their supply chains.
2. Delivery Management
APIs are being used to integrate delivery management systems with other logistics systems. This allows logistics companies to optimize delivery routes, track inventory, and manage warehouse operations more efficiently.
3. Freight Management
APIs are also being used to create freight marketplaces where shippers and carriers can connect and arrange for transportation. This allows shippers to find carriers more easily and carriers to find more business opportunities.
4. Shipping Cost Calculation
Logistics companies are using APIs to calculate shipping costs in real time. This allows customers to get accurate shipping cost estimates before they place an order, improving transparency and reducing surprises.
5. Customs Clearance
APIs are being used for automating customs clearance processes. By integrating with customs authorities through APIs, companies can streamline the clearance process and reduce the time and cost associated with manual paperwork and inspections.
Why Modern EDI Logistics Software is Critical for Business Success
Cleo Integration Cloud eliminates the frustration that comes from onboarding new trading partners because it leverages previously created project templates via its EDI platform to speed EDI mapping processes, and also removes custom-code and one-off integrations. Additionally, Cleo Integration Cloud bridges the gap from a traditional EDI model to one with full connectivity, visibility, and support. By automating the complete EDI logistics software process for automation of EDI document types to ERP/TMS/WMS and other backend systems of record, Cleo delivers more timely information and greater clarity for rapid decision-making...
The right integration platform can seamlessly orchestrate your data to ensure you have complete visibility and can easily maintain compliance.
Here's how a modern logistics data flow might look like with the right integration platform to orchestrate the entire cycle:
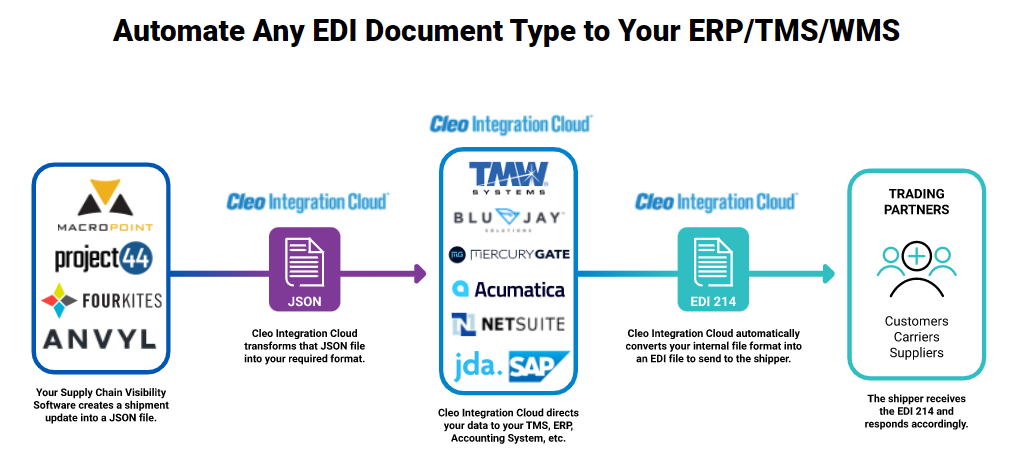
Cleo Integration Cloud elevates a logistics company's EDI visibility over business processes and streamlines its B2B communications. Cleo Integration Cloud helps automate EDI processes in order to connect, transform, and route EDI and non-EDI transactions through its ecosystem without piling on the custom code.
Powerful EDI compliance capabilities are available through Cleo Integration Cloud, which was built to create control in logistics, freight, and trucking by handling all of your EDI transactions in one place. Enabling real-time EDI transmission of crucial forms to your customers or trading partners. Accurate, secure, and accelerated data exchanges provided by Cleo make freight billing easier and enable your expanding freight or trucking business, brokerage, or private fleet to stay up with many of the biggest players in the transportation sector.
Cleo has helped thousands of companies around the world optimize their digital ecosystems by improving processes and operations regarding integrations, data collection, error resolution, onboarding, API + EDI support, and more. Check out what real logistics, 3PL, and transportation Cleo customers have to say about our products and services.
Listed below are two examples of logistics companies that saw tremendous success after partnering with Cleo and using our innovative technologies.
Cleo Customer Success Story: Verst Logistics
Third-party logistics (3PL) provider, Verst Logistics, came to Cleo in 2020 with outdated legacy systems that prevented company growth and process optimization. By using these legacy systems, Verst was experiencing:
- Limited connectivity methods and file type support
- Slow response times and high SLA violation rates due to batch processing
- No ability to update customers in real time about their orders and shipments
Working with Cleo though, the two companies embarked on a year-long migration project—swapping out Verst's legacy systems for a modern EDI ecosystem integration platform. By partnering with Cleo and implementing Cleo Integration Cloud (CIC), Verst Logistics was able to:
- Use API-based integrations to respond immediately to trading partners, ship products to customers faster, and replace batch processing
- Reduce service level agreement (SLA) error rate from 4% to 0.24% — a 94% reduction resulting in fewer fees and more positive customer relationships
- Quickly set up new connections with current and new customers since CIC supports a vast assortment of leading EDI document types, protocols, and standards
- Utilize Cleo's flexible blended services model to meet customer demands when short on internal resources
Cleo Customer Success Story: Giltner
3PL provider, Giltner, came to Cleo in 2020 when the organization realized it was having difficulty scaling due to a lack of control. This lack of control stemmed largely from inadequate self-service options, meaning Giltner had to rely heavily on outside parties to complete revenue-critical integration tasks. Other issues that stemmed from this lack of control include:
- Slow customer onboarding
- Poor integration between systems, which resulted in sub-par data collection and accuracy
- Limited visibility into supply chain processes and transactions, making it difficult to identify and fix errors promptly
To address these issues, Cleo helped with the initial setup to get Giltner up and running on the CIC platform. Cleo still occasionally helps out when Giltner does not have the internal bandwidth for certain projects, but otherwise Giltner has become fully self-service. By harnessing CIC, Giltner was able to swiftly tackle all integration and EDI challenges while simultaneously making vital operational improvements, including:
- A 95% decrease in onboarding time—from eight weeks on average to three days
- A 92% increase in the total number of customers onboarded annually— from six to eight customers onboarded annually, to six to eight customers monthly
- Visibility into errors, allowing Giltner to proactively fix issues
- Integrating B2B transactions into various TMSs across all businesses
- Scale business operations when demand rises
What you will achieve using Cleo Integration Cloud for Logistics:
- Meet performance expectations/decrease customer dissatisfaction
- Meet any customer/carrier need with format, syntax, and protocol depth
- Take action ahead of long-term supply shocks
- Accelerate onboarding of trading partners for faster time to revenue
- Break through application silos and consolidate your integrations
- Pinpoint exceptions, address route cause, and quickly address issues

About Cleo