Top 8 API-Based Integration Use Cases for Logistics Companies

Cleo has thousands of customers in the logistics arena (some of their reviews can be found here). In this new blog series, we'll focus on how logistics companies are embracing integration technology to evolve their ecosystems. These logistics organizations are winning because they are embracing the use of not simply APIs or EDI, but a combination of the two, on one integrated platform.
Introduction
The logistics industry is at the epicenter of digital transformation as consumer buying rapidly shifts to e-commerce channels and supply chains become increasingly global with an explosion of ecosystem participants providing goods and value-added services.
The acceleration in digitalization has caused massive supply chain disruption with technology-driven upstarts such as Uber Freight, Convoy, uShip, and Hwy Haul all sensing an opportunity to disrupt and take market share away from the established players.
As logistics companies strive to differentiate from each other, real-time information is what provides the ultimate competitive advantage. This is especially true in third-party logistics (3PL), where the real value-add is in improving efficiencies across the supply chain. This is because the demand for end-to-end supply chain visibility (from the time a shipment leaves a warehouse until it is placed on a retailer's shelf) has dramatically increased.
Success requires 3PLs to be able to provide fast and actionable two-way exchange of data and information across shippers, carriers, and other value-added ecosystem players in the supply chain. Yet the carriers too are facing increased pressure, both from shippers and 3PLs, to provide real-time actionable insights across the extended supply chain.
So, the question is...
How do logistics companies get the real-time information capabilities they need?
Answer: APIs.
A core enabler of digital transformation, application programming interfaces (APIs) enable real-time, two-way connectivity and communication.
Further, the flexibility, scalability, and speed make logistics API integration a game-changer for the industry which depends on accurate, timely, and actionable information.
Before we get to the why and how on this, let's look at EDI's role to this point.
Role of EDI in Logistics
EDI has been the foundation of supply chain integration in logistics for a long time.
The common transaction sets include EDI load tenders, EDI statuses, EDI freight bills, etc. Today, there are hundreds of carriers that only publish their data via ASC X12 EDI.
For example, if a shipper is looking for carrier status, they would look at an EDI 214 status message and the X12 provides a guide to start the field EDI mapping process.
Since many shippers, 3PLs, and carriers have an established EDI-based load-tender-to-invoice process already integrated to their internal applications and reporting systems, EDI is often the proven low-cost option for supply chain integration.
When dealing with APIs, however, there are no such standards involved; system designers can do whatever they want. However, the EDI X12 transaction sets are a good place to start. As an example, an X12 tender has carrier ID, equipment, ship-to location, etc.
Typically, we find that if a carrier has an API for tender, they have generally the same fields in their API as those that exist in the EDI transaction set.
Essentially, we are passing the same data back and forth, and what changes is the way we pass the data - EDI is typically batch, whereas API is real-time.

See Our Platform in Action
Watch a quick demo to learn how you can automate EDI & API, onboard parters faster, and directly integrate into any TMS/WMS.
Importance of APIs in Logistics
At a basic level, in order to enable the load-tender-to-invoice process across a shipper (3PL) and carrier, shipping APIs do the same exact thing as EDI. The difference is, again, that API implies real-time two-way communication compared to traditional EDI, which is generally batch in nature.
In addition, with JSON or the XML APIs, additional data sets that are not restricted to the EDI format can be passed between participants.
A good example is the exchange of Proof of Delivery (POD) documents between the carriers and the shippers or 3PLs. While there is no EDI format to exchange PODs, APIs allow such documents to be passed back and forth, affording a lot more flexibility.
Another area of exceptional value created by APIs is the exchange of location data during transit to allow for better coordination across warehouses, factories, and retail stores.
Finally, exchanging data with ERPs, TMS, WMS, and finance systems is generally difficult with X12 standards because application-specific APIs are required to seamlessly integrate in real time with such back-end applications.
Today, given the rapid digitalization and growth of e-commerce, logistics companies are realizing the potential of APIs for connecting suppliers, carriers, cloud providers, and SaaS applications.
While EDI is established, proven, and low cost, API-based integrations are growing at a rapid pace to both:
1. Complement traditional EDI for real-time information exchange, such as location data, trucking spot rates, etc.
2. Replace EDI with API, especially when 3PLs and digital freight brokerages (DFBs) are leveraging APIs in their platform as well as technology-enabled TMS and WMS applications.
For these reasons, the rate of adoption of APIs in supply chain management has grown far faster than EDI and the pace of growth is about to accelerate even more.
All that said, I believe the top eight API-based integration use cases explained below can dramatically enhance competitive differentiation for logistics companies:
1. Load-Tender-to-Invoice Enablement
The entire EDI-based load-tender-to-invoice process can be replaced by an equivalent set of APIs for real-time information sharing.
Especially with API-enabled TMS systems, the load tender APIs can be immediately sent to the carriers and with real-time two-way communication, the 3PLs and shippers can optimize their supply chain more efficiently.
APIs also enable automated billing between carriers, shippers, and 3PL partners; and that can reduce errors and ensure timely payments.
Lastly, APIs can also allow carriers and shippers (3PLs) to pass POD documents back and forth, which provides significant value for efficient supply chain integration.
2. End-to-End Visibility and Real-Time Tracking
Logistics companies are using APIs to provide real-time tracking information to their customers. By using APIs to share data between different players in the industry, companies can provide customers with real-time updates on the status, location, and route of their shipments, as well as optimize their operations by improving visibility and control over their supply chain.
APIs can directly connect with electronic logging device (ELD) aggregators, visibility providers such as project44 and FourKites, and mobile applications.
3. Accurate Spot Rate Information
APIs can link shippers and 3PLs directly to carrier online services, allowing them easy access to accurate up-to-date spot rate information.
While shippers in recent times have preferred contracted rates as a safe option given the shortage of truck drivers, capacity crunch, and new hours of service (HOS) regulations, in reality, spot rates can be lower at times making them more optimal.
Given the technological advances in freight management, many shippers are striving to strike the right balance between the use of contracted rates and spot rates while lowering overall cost and contractually staying compliant with contracted rates to avoid fines and financial repercussions from carriers.
4. Automated Freight Matching Enablement
APIs can also enable shippers and 3PLs to query multiple carriers to determine their most cost-effective routing options in real time.
Historically, freight matching was done by going to each site manually as well as leveraging traditional methods such as phone, email, and fax.
APIs can make the entire freight-matching process far more efficient through end-to-end automation.
5. Back-End Application Integration
APIs are invaluable when companies have back-end applications (SaaS and legacy/on-prem) that need to be seamlessly integrated into a digital load-tender-to-invoice process as well as the ability to extract in real time up-to-the-minute spot rate, location tracking, and routing information to enable digitalization of supply chain processes.
APIs also allow a new level of customizability. As an example, SaaS applications may not have the exact interface needed for a given logistics business case. But by leveraging API-based integration capabilities, like shipping APIs for eCommerce, a customized extension to support the required business case can be efficiently developed and deployed.
6. Shipping API Integration
API integrations can connect applications and platforms within a logistics provider's digital ecosystem, allowing for both the real-time transfer of data and updates regarding a shipment. This includes API integrations internally, as well as externally to customers and trading partners. Examples include API integrations with:
- eCommerce websites
- Warehouse management systems (WMS)
- Transportation management systems (TMS)
- Delivery management systems (DMS)
- Order management systems (OMS)
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
7. Freight Marketplaces
APIs are being used to create freight marketplaces. Freight marketplaces are online matching platforms that connect shippers with logistics providers. By using the platform, shippers can find and select carriers that can fulfill their service needs—i.e. being able to ship an order from point A to point B within a certain timeframe.
Freight marketplaces are a great option for both shippers and logistics providers because it helps both parties discover more business opportunities, while also negotiating the best price for the service.
8. Custom Clearance
APIs are being used for automating customs clearance processes. By integrating with customs authorities through APIs, companies can streamline the clearance process and reduce the time and cost associated with manual paperwork and inspections.
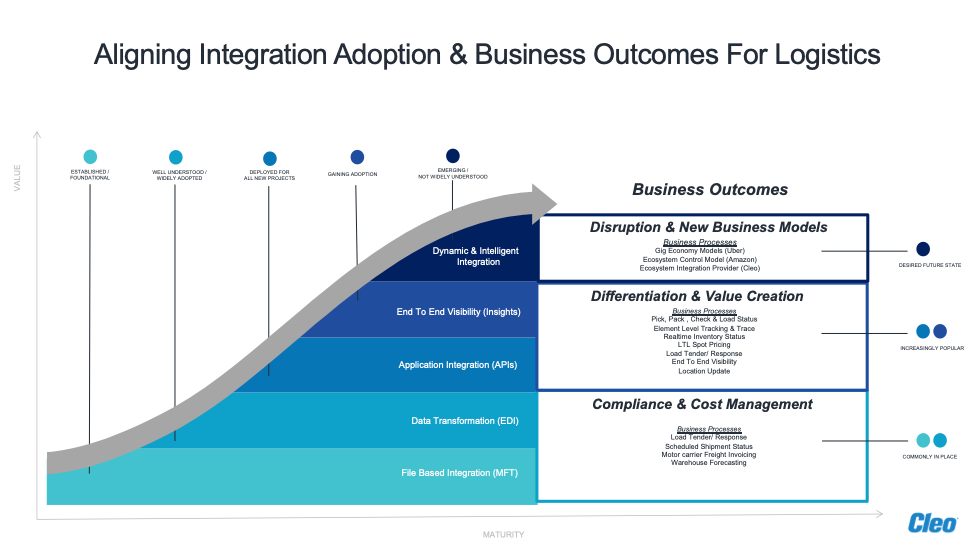
Fig. 1 - Cleo's Maturity Model for aligning integration adoption and business outcomes for logistics companies
A maturity model approach (see Fig. 1 above) can help significantly in rolling out a digital transformation program for logistics companies with well-defined business releases tied to clear metrics and KPIs.
I will explain this framework more in-depth in a future blog in this series. For now, suffice it to say that the ability to continuously create and deliver business value - no matter where one is starting from -- is critical for getting firm-wide adoption of the digital transformation program. And based on our integration expertise across some 1,000 transportation and logistics companies, we recommend the five-stage ecosystem integration maturity model for shaping your go-forward plan.
What are your thoughts about APIs for accelerating growth and preparing your business for the digital future?
Learn More About API Use Cases
Learn about the benefits of leveraging APIs for common Logistics & Transportation use cases, including L2I Transformation, Real-Time Shipment Visibility and Tracking, and more.
If you want to get ahead by enabling real-time, two-way connectivity and communication, you should explore Cleo Integration Cloud: a platform that combines powerful API integration capabilities and end-to-end visibility.

About Cleo