Blog: Data Integration and What to Know Before Starting a Project

Within an enterprise, data is coming from every angle imaginable. Various sources are sending different types of data, in all shapes and sizes, and the onus is on enterprise IT to integrate that data in an easy-to-manage way. So how exactly does a business handle all this data in a modern manner? More often, organizations choose to deploy a data integration software that flexibly connects the systems and applications powering their critical information flows.
What is Data Integration?
Data integration is the process of combining data from several different sources into one unified view, to make the data more actionable and valuable to an enterprise. Data integration software achieves consistent access and delivery of data across different business processes to meet the information consumption requirements of all applications.
While there is no universal approach that is a one-size-fits-all fix to data integration, most solutions feature a few common traits, such as a network of data sources, one master server, and clients that access data from a master server.
The History of Data Integration
Data collection has always been a challenge, especially when computers first started rolling out because there were zero methods in place. This started to change in the early 1990s after the University of Minnesota created one of the first data integration systems. The integration system harnessed data warehousing, along with extract, transform, and load tools (ETL). ETL tools pull data from one location, transform the data into a form that a different application can understand, and then loads the data into the other application.
As time went on, new data integration issues appeared. These include data quality, governance, modeling, and data silos. Data integration became a necessity for business operations when the Internet of Things launched in the early 2010s. Largely because a massive influx of devices, apps, and platforms were now being connected to the internet and were capturing data. This massive increase in data capture led to what we now call ‘big data'. There were a myriad of devices that could suddenly capture data, but companies had no idea how to sort this massive ingestion of disconnected data.
Thus, data integration was born from ETL. Over the years the technology has evolved to become more user-friendly and intuitive, giving users more control and visibility into their data integration processes. Flash-forward to today and companies have a medley of data integration software to choose from to suit their business needs.
How Does Data Integration Software Work?
Are you wondering how to do data integration? Data integration primarily works via three main steps that are part of the ETL process.
1. Extract: Data is extracted from the source and placed in a temporary location where it is cleaned and undergoes quality assurance
2. Transform: Data is transformed into a format that the end destination system can understand
3. Load: Transformed data is ingested into the data warehouse, data lake, or other system, or platform for storage, safe-keeping, and analysis
Businesses can then use this accurate, integrated data to make strategic and informed decisions.
What Can Data Integration Fix?
The importance of data integration continues to grow for a few reasons. The first is that accurate, real-time data is becoming increasingly vital as companies use data to make strategic business decisions. Secondly, the overall quantity of data collected is increasing which makes data organization more crucial than ever.
Not only is data integration helpful for those reasons, but it can also help organizations address other issues. These issues include big data, data silos, semantic integration, and accessibility.
Big Data
Data is an invaluable asset to businesses. However, most companies collect far more data than they analyze, letting precious insights go to waste. Data integration software extracts and combines data that would otherwise never be utilized, and organizes it in a manner that users can easily analyze. Integrating big data can help organizations optimize their processes and supply chains, better target customers and understand their behaviors, and uncover issues, new findings, and opportunities.
Data Silos
Data silos are collections of data that are only accessible by one user, team, or department within an organization. One of the easiest methods of removing data silos is to leverage data integration. Data integration software will extract the data from the source of each silo, transform the data, and load it into the central repository. This allows users from any department to access company-wide data, as long as they have system access to the central data warehouse.
Semantic Integration
Semantic integration extracts data from different sources, combines it, and then organizes the data in a way that users can analyze. Data integration helps pull and transform the data from various locations. It then features the blended data in a central location for users to view and analyze.
Accessibility
Similar to the above three points, data integration promotes accessibility. With data integration, users can access data from various teams, departments, sources, and systems, all from a central location. Furthermore, if the data is stored in the cloud, users can access the data from any device connected to the internet, as long as they have the proper login credentials and are granted access by the system administrator.
Benefits of Using Data Integration Software
Data integration software efficiently aggregate data and then make it available to anyone that needs it. There are many various benefits for a company using a data integration solution.
Different types of data mean different levels of specialty that the dataset gains. Each set of data has unique attributes, everything ranging from metadata, structure, and schema. Integration solutions support all such datasets and attributes.
Specialized applications serve a variety of business information needs, but they also open new opportunities to take advantage of data in new ways. Data integration enables users to convert between formats and open data in legacy or cloud data integration services and leverage the information these systems provide.
Data becomes less complex. Data integration manages the complexity that comes from data migration and streamlines those connections to make it easy to deliver that data to any system. If properly integrated, there is no need to replicate data across disparate applications.
Data becomes more valued than ever. Users can now break down their internal data and merge it with external data and combine structured and unstructured data from many different sources.
Data is more centralized. By centralizing data, it becomes simple for anyone in the company to access it. Centralized data also means data is more easily transformed than it was before data integration.
Collaboration within data also becomes improved because of its accessibility. Now employees can share data internally or across their organization more easily.
Data accuracy is much improved. It becomes more consistent and is mostly free of errors to ensure that the data is valid and viable.
These are some of the ways that an enterprise can truly take advantage of a legitimate data integration strategy. Without a set plan in place, it becomes much more difficult to manage, but with the right strategy, companies realize significant business value from a data integration solution.
Typical Business Use Cases for Data Integration
What are some of the ways you can put data integration into action and realize the promise that makes it so appealing in the first place? Here are a few ways savvy organizations use data virtualization solutions:
Leverage Big Data
Big data analytical solutions offer a way to gather valuable information from your structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. Big data integration allows enterprise IT to integrate and combine all data at once and prepare it for analysis and help gain insights necessary to make valuable business decisions that affect the bottom line. It doesn’t matter what kind of data that IT needs to break down and analyze, whether it’s traditional data, machine-generated data, social media, data from the web, or data from the Internet of Things networks, data integration allows for the real-time, quick ingestion of data.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
One popular way that enterprises take advantage of data integration is through customer relationship management (CRM) software. CRM allows an enterprise to capture and gather information about their customers who are interested in your products. Through data integration, it is easier for an enterprise to identify and target their customers and also reap value-generating benefits, including up-to-date records that reflect accurate customer information, managing a database of sales leads that can be tracked and monitored throughout the process, and identifying future opportunities to approach or partner with customers.
Visibility, Visibility, Visibility
It is often difficult to recognize the true value that a single piece of data represents. But thanks to data integration, it’s easier to track and monitor data throughout an entire business process, and the business value from data is readily visible. A business user, for example, can see a complete customer view – from the ordering process through fulfillment – that was built within a data integration solution in the form of data synchronization. Data integration takes all that customer’s information and it collects, prepares, and delivers said data in a way that is easy to digest and follow, no matter what kind of data it is.
Business Intelligence
Effective business intelligence has a certain number of requirements, so data that goes into a data warehouse needs to be repurposed a fair amount to successfully create an aggregated and calculated data set. Data integration tools collect data and transform it to meet all these required structures so that a business intelligence solution can run the way it is supposed to. In doing so, data integration also leverages key business processes such as business performance management, reporting, dashboards, and advanced analytics to enable some valuable strategic and tactical strategies.
Types of Data Integration Approaches
There are multiple ways that a company can choose to utilize data integration technology, with approaches that each represent functionality that the others do not. Which approach you choose to take to data integration will depend entirely on your requirements and what it is you want to get out of data integration.
Data Consolidation
Since within an enterprise, the amount of data that needs to be moved and transformed can become so large, it also becomes heavier and more complex, which requires more resources. So, enterprises must have the ability to consolidate to simplify data access.
Data Warehousing
Data integration also can be part of a data warehouse, another way to synchronize and consolidate data. This specifically comes in handy for business intelligence users by providing them with adequate data for further analysis that can separate online analytical processing (OLAP) from online transaction processing (OLTP).
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL)
Much of the data that an enterprise needs to integrate are extracted, transformed, and loaded (ETL). This approach coincides with data warehousing because the data warehouse pulls in all the data from various sources and then converts it into a common format so each set of data is compatible with the other. From there, the new data is loaded into its new database. Once the query has been submitted, the data warehouse finds the data, retrieves it, and delivers it to the user in an integrated view.
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
An iPaaS – or Integration Platform as a Service – provides a centralized console to manage, govern, and integrate cloud-based applications, using tools that connect cloud applications and services and control integration flows. Companies use iPaaS solutions to scale performance needs, add product functionality, and structure application integrations, all to increase the value of their business relationships.
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
An enterprise service bus (ESB) is a critical component of internal data integration. An ESB is designed to integrate various applications over what is a “bus-like” infrastructure. An enterprise service bus usually is located somewhere between the framework and a suite as another way to perform application integration. An ESB is a middleware tool that distributes tasks among the connected components that make up an application.
The Challenges of Data Integration
While there are many benefits to using a data integration solution, regardless of what kind of approach and style that a business selects, there are some challenges. The average business would not be considered a data integration specialist, and some pratfalls must be avoided to truly reap the rewards that come from data integration.
Because an environment filled with data from all kinds of different sources can be so complex, that presents an inherently difficult challenge to manage. With data coming from every direction and in a variety of formats, data mapping is critical to synchronize your data successfully without a bunch of custom code and without overwhelming your internal resources. Data transformation technology automatically maps data from one source to another to facilitate communication and integrate each application.
Additionally, over time, data sources updated at different intervals can lead to invalid data that’s of little use to the business. Programming your integration solution to aggregate data from multiple sources into a usable product requires common consistency among definitions and rulesets.
And thus, it’s critical to select a trusted data integration solution provider for your integration projects that can clear obstacles and overcome challenges that tend to disrupt business. An expert partner will help manage all the complexities and potential hiccups – from deployment to implementation – and help you maintain the data quality your business needs to run smoothly.
How to Choose the Best Data Integration Software: Types of Tools
When it comes to data integration software and technology, there are two main options — on-premise and the cloud. Both options have their own set of advantages and drawbacks, thus the better option depends on each company's individual goals and needs.
On-premise Data Integration Technology
On-premise data integration software and hardware is implemented, monitored, and maintained locally, instead of using an external vendor. Companies are usually required to purchase a software license for using the technology. We explore the pros and cons of on-premise data integration below.
On-premise Advantages
- Control: Companies can upgrade storage, add platform features, complete updates, fix errors, etc., all on their own accord without relying on outside entities
- Security: On-premise servers may be more secure for sensitive data, as external parties (such as cyber criminals) cannot access the network and software
- Offline Accessibility: Internet connection is not required to access the software, meaning users can access the platform offline
On-premise Drawbacks
- IT Support: Companies need to manage and financially support an in-house IT team to maintain the internal servers and hardware
- Scalability: Businesses must physically install new hardware to allow for additional storage and capabilities, unlike the cloud which only takes a click of a computer mouse
- Investment: On-premise data integration deployment can be expensive as it requires investing in hardware, installation, and maintenance, requiring time and money
Cloud-based Data Integration Technology
Cloud data integration systems are hosted on an outside vendor’s servers. Users can easily access the cloud platform through a web browser, such as Google Chrome. There is no physical hardware or maintenance required on the user’s end, as that is the responsibility of the cloud vendor.
Cloud Advantages
- Accessibility: Users can access the system and its data 24/7 from anywhere, as long as there is an internet connection
- Pricing: There are no upfront costs with the cloud since no physical infrastructure is required—users only pay a subscription fee which usually includes maintenance and support
- Maintenance: The vendor is responsible for maintenance and updates
- Scalability: Companies can nimbly scale operations since the technology is in the cloud, rather than having to swap out physical hardware like on-premise solutions
Cloud Drawbacks
- Internet Dependency: If the internet goes down or users do not have access to an internet connection, they cannot enter the platform
- Limited Customizability: The data integration vendor handles updates, limiting the ability of personalization cloud users can perform
- Security: The cloud has countless security features in place, however utilizing outside vendors for file and data storage provides companies with less control over cybersecurity
What is a Data Integration Cloud?
A data integration cloud is a repository of data from disparate sources that are collected and blended. This data is located and stored in the cloud for users to access via the internet. There are many benefits for businesses utilizing a data integration cloud, including automating tasks and greater data control.
Automated & Centralized Data Control
Automated data control is the process of automatically collecting and blending data using data integration technology. This is done by integrating various systems, platforms, applications, and software.
Centralized data takes the extracted data collected from the integrated systems and transforms and loads the data into one central location or repository. This could be an on-premise or a cloud-based integration platform.
With automated and centralized data, users do not have to manually open and search through each platform to find the information they are looking for. Instead, all the key data and information are conveniently located and organized in one location. Automated and centralized data control has many advantages, including:
- Efficiency: Users can quickly find the information they are looking for
- Productivity: Users spend less time hunting for data and have more time to complete other assignments
- Real-Time Data: Data is collected and updated in real-time, so users have the most up-to-date information
- Accuracy: Data is collected by technology, removing the need for error-prone humans to manually pull the data
- Optimizing: Since data is neatly organized, users can better analyze the information and deduce helpful findings
- Security: Companies can better monitor their data since it is stored in one location instead of countless individual platforms, making data management more manageable
Why Do Businesses Choose Cleo Integration Cloud?
Key to a successful digital transformation strategy, data integration can reshape how your business uses technology to interact with customers, vendors, suppliers, and applications. The functionality gained from such a powerful business solution provides the operational efficiency to rapidly and securely exchange data among internal systems and external trading partners.
Cleo Integration Cloud (CIC) enables the world’s leading organizations to accelerate cloud-to-cloud and cloud-to-ground integration processes to easily integrate applications, data storage repositories, and business platforms. Through Cleo data integration, all your data is connected in an elegant way that better powers your cloud, on-premise, or hybrid environments and delivers more value to your business and your end customers.
What can you achieve with Cleo Integration Cloud?
Design and build
- Accelerate the creation of dynamic end-to-end business workflows
- Streamline data transformation, orchestration, and movement processes
- Low code to build enterprise data integration processes
Operate and optimize
- Orchestrate and automate dynamic multi-enterprise data integration workflows
- Quickly connect and integrate data across new applications and partners
- Elastically scale data integration flow capacity to meet peak performance demands
Drive business intelligence
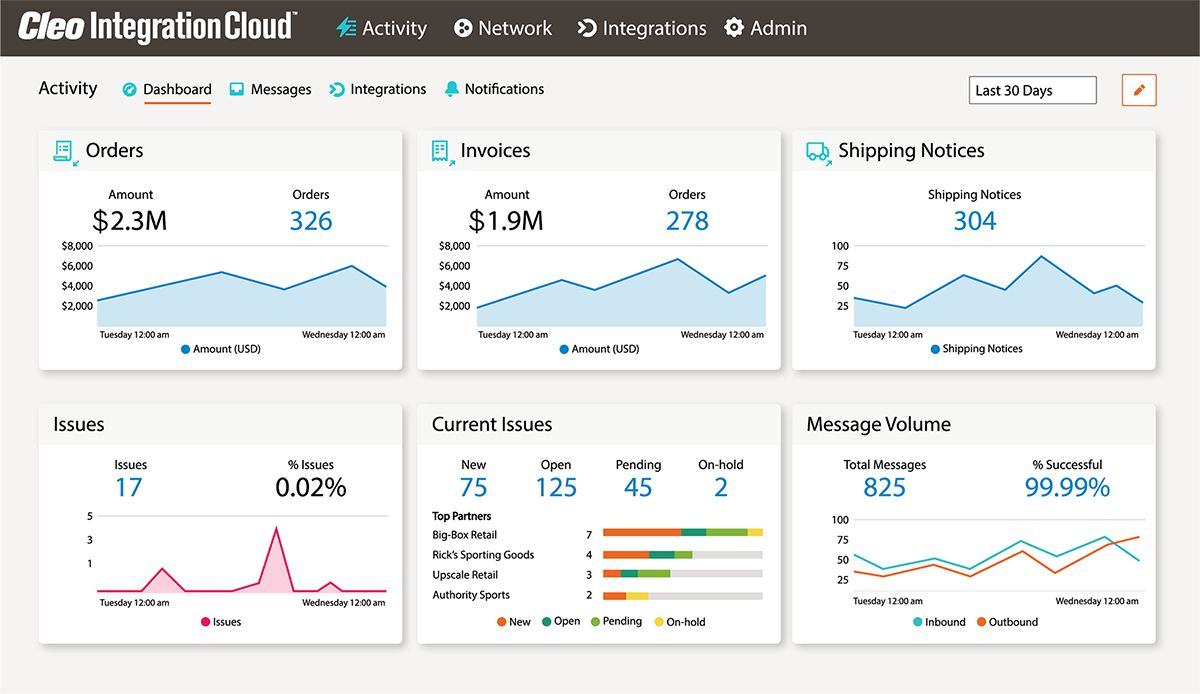
- Deepen the context of end-to-end process flows and enable greater insight with Cleo data integration
- Visualize operational data with real-time business process activity views, anywhere and at any time
- Tap into powerful persona-based insight across business and operational ecosystems
Want to learn more? Take the next step of your data integration journey by accessing the Cleo Integration Cloud demo video library.

About Cleo
Watch a Demo

Comprehensive Guide to Gaining B2B Control

Duraflame Case Study