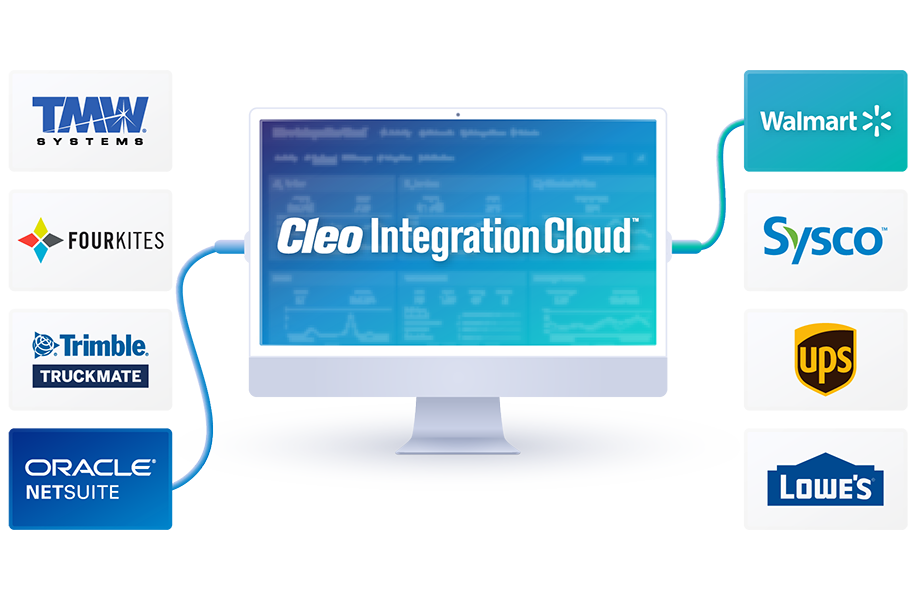
EDI Integration & Why It’s Important to Your Business

Here is everything you need to know about EDI integration:
- What is EDI Technology?
- What is EDI Integration?
- How EDI Integration Works
- EDI Integration Requirements
- Why EDI Integration?
- What are the Advantages of EDI Integration?
- 4 Future Trends in EDI Integration
- 4 Indications Your EDI Integration Is Broken
What is EDI Technology?
Simply put, EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) technology allows the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in a standard electronic format between different business partners. The perks of moving to an EDI platform that specializes in EDI integration include:
- Reduced costs
- Automated workflows
- Faster document transmission and transformation
- Fewer errors
- Smoother relationships with partners and customers.
EDI transactions contain critical information for business exchanges, and a popular example of an EDI in action is that of EDI order processing.
So, how does EDI work?
First, a buyer submits a purchase order for a product from a supplier, next the supplier sends an invoice, and finally, both parties exchange acknowledgment receipts.
In the example EDI exchange below, Business A is purchasing a widget from Business B:
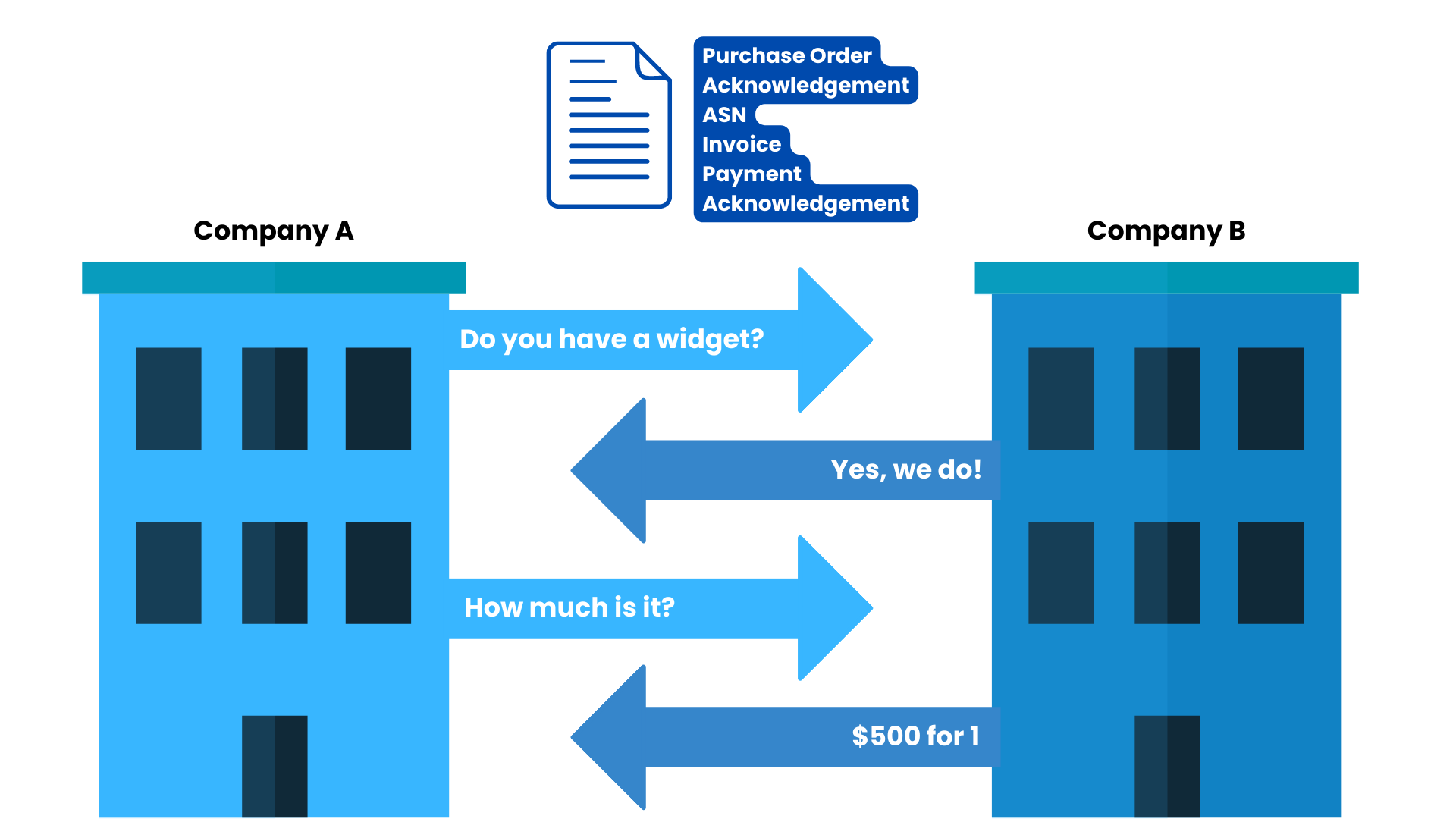
Another common EDI transaction referenced in the diagram is an advanced shipping notice (ASN), which is a notification of pending delivery. Its primary purpose is to provide tracking and packing information ahead of delivery. Located within an ASN are a purchase order number, ship notice numbers, and the location where the product will be shipped.
What is EDI Integration?
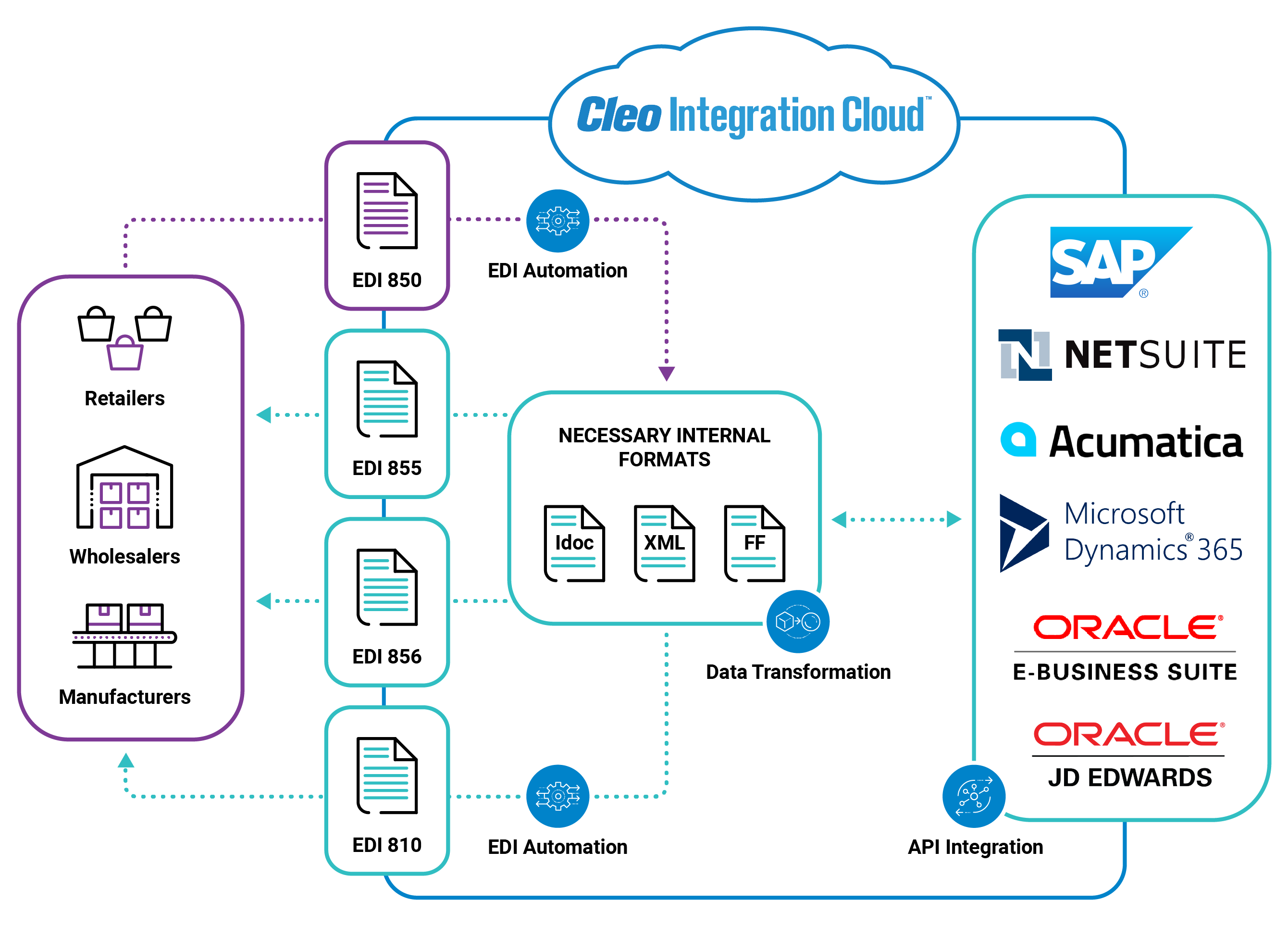
EDI (Electronic data interchange) integration is the electronic communication of business messages (orders, invoices, credit notes, ASN's, etc.) from your own EDI system to your own back-office, warehouse, CRM, or ERP systems, which eliminates having to re-key business information. Trading partners use EDI integration to streamline communications with customers, vendors, and other business partners. The process involves mapping the data fields of EDI documents to the corresponding fields in the target system or application, such as an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, a warehouse management system (WMS), or a supply chain management (SCM) system. This ensures that the data is accurately transferred between systems, minimizing errors and enabling seamless communication between trading partners.
EDI integration is created when an EDI workflow is established between trading partners. Moreover, it can be achieved through two steps:
1) Establishing the EDI documents, protocols, transactions, and endpoints that you will use to exchange data with your trading partner
2) Converting EDI data into a format that can be used in your own back-end technical environments, such as your ERP system or accounting solution.
In the center of the EDI integration diagram below, data structures are translated into a mutually agreed upon EDI standard format (ANSI X12, EDIFACT, etc.). Translating internal data into EDI files enables both trading partners to speak a common language and communicate with one another.
The EDI files in the center are then converted into a proprietary file (IDoc, JSON, or another ERP-specific format) that can be easily ingested into the back-end systems on the left and the right (SAP, Acumatica, etc.)
How EDI Integration Works
While the technology itself has been around for decades, many organizations now are seeking EDI integration software and solutions for EDI modernization initiatives, which can extend EDI data integration and automation capabilities beyond a traditional EDI message to support emerging business requirements. It is critical for enterprises to find EDI integration software that delivers an integrated approach for delivering automated workflows, increasing EDI visibility into operations, and improving customer service, regardless of the industry.
Step 1: A sender exports a business document from an in-house system or application. A common example is a purchase order to buy goods or services.
Step 2: The business document, in the example diagram below, a purchase order EDI cycle, is converted from the in-house computer system into the required EDI format through data transformation mapping software or any of the various EDI translators.
Step 3: The EDI business document is next run through EDI conversion software to ensure that it is structurally accurate based upon the agreed-upon EDI standards currently in place.
Step 4: The data from the EDI document is either transmitted to a value-added network (VAN) via a secure communication protocol like SFTP, HTTPS, or AS2, which can then be built into the same validation software or another application, or it can be transmitted right to the client via a direct connection over similar protocols.
Step 5: Direct EDI over AS2, for instance, creates a secure line between two different businesses, and enterprises can connect to trading partners without any document fees and gain real-time communication capabilities. The receiving party receives the file, verifies the credentials, authenticates the source, and decrypts the file so it can ingest the EDI doc right into its systems. It also sends back a message disposition notice (MDN) to acknowledge delivery.
Another option, if perhaps a bit outdated, is to go through a VAN, which makes a determination how it should route the data and then either switches it to a different VAN that is used by the recipient or delivers it to the VAN mailbox (if the sender and receiver are using the same VAN service). The data has officially crossed over to the receiver, and it is the receiver's responsibility and their VAN service.
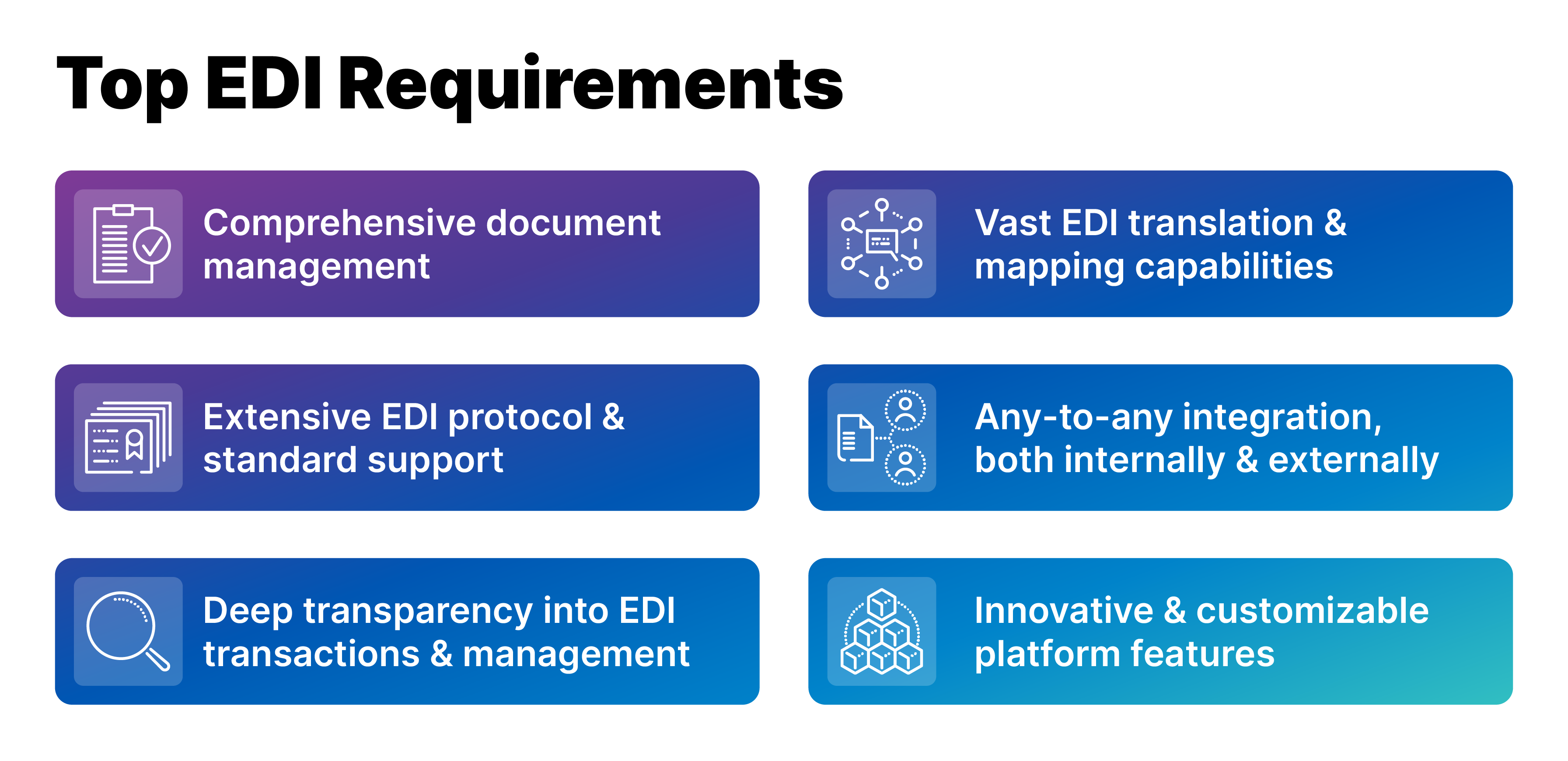
EDI Integration Requirements
Technically speaking, EDI integration has a few requirements.
1. A company has to agree on which transmission protocol to use with each of their trading partners
2. A company has to agree on the message format with each of their trading partners
3. A company needs the capability to export messages from its ERP system and convert them into the agreed-upon EDI message format.
From a project management perspective though, an EDI integration project typically consists of five key stages. These are:
1. Determine Your Project Goals and Mandates
The first step towards choosing an EDI integration solution and provider is identifying the goals and requirements of the project. This may include determining the:
- Processes you plan to automate
- Specifications and requirements of your ERP system
- Evaluating your internal skills and bandwidth
- Identifying your EDI partners
- Necessary document formats
- Monthly volume of messages and transactions
2. EDI Provider Selection
Equipped with a clear outline of your project's goals, you can start researching EDI providers that best align with your company's unique needs. When choosing a provider, it is vital to consider future growth and to thoroughly assess each provider's offerings; especially in terms of support and pricing.
3. Implementation Planning
Creating a comprehensive project plan is essential. Include details such as an implementation timeline, trading partner onboarding list, team member responsibilities, training schedule, etc.
4. Technical Implementation
Establish the transmission channels, protocols, and message formats you will be using with your trading partners. Onboard trading partners and set up integrations. Perform testing. Depending on whether you utilize managed services or a self-service approach, these tasks may be your company's responsibilities or whomever you outsource them to.
Tip: leave the legacy process in place during testing until it is confirmed the new process works without hiccups.
5. Ongoing Operations After your system is operational, continuously monitor it to quickly catch and resolve any errors. Additionally, your solution will likely need routine maintenance, updates, and optimizations to keep it operating at peak performance.
Check out our blog for a breakdown of how to overcome common EDI implementation issues.
Why EDI Integration?
In today's hyper-digital business world, most organizations that need to use EDI systems for their critical B2B transactions are actually already doing just that. But the businesses that are utilizing EDI integration to their fullest potential, are the ones who are truly reaping automation rewards through improved visibility over business partner transactions and the elimination of manual operations.
What are the Advantages of EDI Integration?
There are many different reasons that enterprises continue to use EDI within their enterprise. From saving countless amounts of money to improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency, EDI remains an incredibly useful tool.
- Data accuracy: Automating EDI transmission to your trading partners, along with ingestion and transformation into your ERP eliminates the need for manual data entry. By nature, manual data entry is plagued by errors and the creation of automated data flows prevents mistakes from occurring in the first place, ensuring that you remain EDI compliant.
- Business cycle speed: EDI integration allows your enterprise to cut down processing time. Order-to-shipment business cycles can be reduced by as much as 50-60%. EDI transactions that are exchanged in minutes instead of days mean a faster time to completion.
- Trading partner visibility: EDI integration done right means your business can spend more time focusing on the business. Knowing data is accurate, automated, and easily accessed within your ERP gives you the ability to easily view how your EDI partners are affecting your entire business.
What are the 3 Types of EDI Integration?
There are three types of EDI integration: direct EDI integration, indirect EDI integration, and hybrid integration.
- Direct EDI integration: Direct EDI integration is created using a specific protocol like AS2 or FTP to establish a connection from your EDI trading partners (customers, suppliers, and service providers) to your internal ERP. This specific instance of direct integration is called EDI ERP integration. Oftentimes direct integration results in a business managing thousands of individual partner connections resulting in added complexity, especially if your business doesn't have a standardized protocol. Direct EDI integration is well suited to larger-scale integrations that move lots of data back and forth between ERP and trading partners.
- Indirect EDI Integration: An indirect EDI integration is established through the use of an outside EDI value-added network (VAN) or another type of broker. The VAN acts as the middle man between your ERP and your trading partners. A message is sent from your ERP to the VAN. Once that message is received, the broker or VAN transforms and then sends the message into the necessary format preferred by your EDI trading partner.
Hybrid EDI Integration: In some cases, an organization wants a combination of indirect and direct EDI integration. For example, a VAN might handle some of an organization's EDI transmissions, but critical customers are connected via direct EDI integration. Hybrid EDI integration is essentially a combination of managed EDI services with in-house EDI resources to create a flexible EDI solution.

Level Up Your Supply Chain: Explore Our EDI Solution
You’ve taken the first step towards a smoother supply chain by finding this blog - now discover how our EDI solution automates data exchange, saving you time and boosting efficiency.
4 Future Trends in EDI Integration
According to Chandana Gopal, research manager at IDC, "Enterprises have to continue to invest in modernizing B2B integration software in order to stay competitive in the digital economy." Let's take a look at four trends that stand to impact the future of EDI providers and EDI integration.
- IT Skills Shortage
- E-commerce Growth
- Business System Integration
- Growth of Blockchain Technology
1. IT Skills Shortage:
Cloud computing is rewriting the rules for EDI technology deployment and service consumption models. More businesses are looking to migrate applications, connections, data, and integration to the cloud. This includes cloud EDI. However, as cloud computing has grown to astronomical levels, the need for good talent within an IT department has never been higher.
The London School of Economics estimates that a lack of cloud skills has cost businesses $258 million annually. Cloud computing is designed to provide elasticity, flexibility, and save money, but without the right internal resources in place to handle cloud migration, cloud service adoption, or a cloud-first IT strategy, it's unlikely that the enterprise can modernize critical EDI operations to the cloud unscathed.
When IT departments are faced with a skills shortage, one common approach that many have opted to take has been to outsource. Partnering with an external IT service can reduce costs, overhead, and provide 24/7 coverage that an understaffed or short-skilled IT or integration competency center cannot. Outsourcing the EDI integration skillset means integration competency is no longer an internal requirement. This will inevitably increase the reliability of the digital business transactions, and also provides control over support and services engagement required to ensure successful migration and maintenance.
2. E-commerce Growth:
Without a doubt, e-commerce is by leaps and bounds the fastest growing sector in retail. Online shopping is everywhere, it's become a way of life, and for traditional brick-and-mortar corporations, the allure of jumping into the e-commerce space is too tempting to pass up - if not to reap untold riches, at least as a life raft.
Between the increasingly disruptive Amazon effect and headline-making, paradigm-shifting acquisitions in the retail space, the e-commerce explosion continues to have a very powerful impact on multiple industries.
As the e-commerce growth in the market expands by record margins, a new challenge begins to present itself. And that challenge revolves around the ever-increasing complexity of data and the sheer volume of data e-commerce business processes produce. Because an e-commerce business model depends on many different technologies, from supply chain management solutions to application, data, and B2B integration capabilities, the end result is a very complex environment.
E-commerce supply chain data has an interesting composition. The data comes in all forms, from customers, partners, and retailers. The challenge that enterprises face is around data access, integration, and management. That's why a modern B2B infrastructure approach is more important than ever, and not something that enterprises should undervalue or take lightly. Even enterprises that have a tentative handle on their current data demands recognize the cascading complexity in the near future. Often, existing technology is more stable and should be considered first when looking to address new and upcoming challenges relating to the e-commerce boom.
EDI is a foundational technology at connecting ecosystems for the seamless flow of supply chain, inventory, and retail data. EDI continues to act like the existing communications standards for most industry-specific supply chains.
See common EDI standards throughout the world below:
EDI Standards
- ANSI ASC X12 or X12 for short represents EDI standards for finance, transportation, supply chain, and insurance in North America
- EDIFACT is a common standard outside of the US
- RosettaNet, based on XML, is used broadly in the supply chain, manufacturing, and services industries
- GS1 EDI is used in retail globally
- TRADACOMS or GS1 UK is dominant in retail in Great Britain
- ODETTE is the standard used by the European automotive industry
- HL7 required by HIPAA regulation is predominant in US healthcare
Go anywhere in the world and you can use EDI to conduct business, therefore, the growth of e-commerce is providing a new area of expansion and implementation for EDI.
3. Business System Integration:
Modern EDI offers extensive capability benefits in and around business system integration.
The benefits of modern EDI include:
- Any-to-any format transformation, data mapping, and integration
- Action orchestration for intelligent automation
- Asynchronous, synchronous, and real-time transactional capabilities
- Visibility and analytics capabilities that serve operational and business intelligence use cases
- Extensive integration capabilities for on-premise and cloud applications, systems, data, and partners
To underline the importance of business process integration, consider the example of digital modernization:
In this day and age, businesses need the ability to conduct business system integration quickly and efficiently to increase business agility. That's why many upgrade modernize enterprise resource planning (ERP) software in order to better conduct business with greater flexibility and reliability. But ERP cloud migration is complex, costly, and risky if done without a guiding strategy that includes business system integration. That's where EDI, or rather, modern EDI comes into play.
EDI must coincide with integrated business endpoints with ERP systems and other core business applications that run the enterprise. It's EDI that connects the data, applications, trading partners, and underlying revenue-generating business processes. Across every back-office system, from the enterprise financial solution to your customer relationship management (CRM) program, EDI provides a versatile toolset to ensure business process integration.
4. Growth of Blockchain Technology:
It seems like every few years or so, the latest and greatest technology appears, and all of a sudden, everyone says it's going to replace EDI. Years ago, it was XML. A few years back, it was APIs. Now? Enter blockchain. Even Gartner recognizes that the mechanisms of industry hype have promoted blockchain to a fever pitch before its time has realistically come for most businesses.
The truth of the matter, however, is that while blockchain is effective for certain types of actions, it will not replace all B2B transactional technology. If anything, blockchain technology will only stand to augment existing EDI systems and work hand-in-hand with them.
The end result is that the way enterprises currently conduct B2B transactions does not necessarily have to change drastically - if at all. In fact, it can continue to operate the way that it has, while at the same time, blockchain can add an increased amount of visibility between three parties that only makes EDI a more powerful technology.
In 2019, EDI and XML accounted for approximately 88%-95% of all B2B transactional volumes. While blockchain represents a disruptive force, the fact is that EDI remains ingrained in transacting everyday business actions across every industry, making EDI a natural fit as a component in any B2B integration technology stack.
As Ken Vollmer, former principal analyst at Forrester described EDI: "Its ongoing growth means it will continue to be the dominant document exchange alternative for many years to come."

Ready to Take Your EDI Research to the Next Level?
You've explored the benefits, now see how it applies to you! Get a personalized consultation on how our EDI solution can streamline your supply chain. Just provide some information for a free, no-obligation assessment.
4 Indications Your EDI Integration Is Broken
Relying on outdated and often disparate solutions simply does not provide organizations with the ability to best serve their customers, and stay one foot in front of the competition. It's never easy moving away from something you're comfortable with, but the business benefits gained from a modern integration platform are remarkable, both in the short and long term.
EDI remains the most common and widely used standard for B2B transactions. But if you're one of those organizations (and there are a lot of them) that remains in a legacy environment, odds are you're having difficulty supporting EDI integrations.
If that is the case, i.e., if you can't support end-to-end EDI integration, here are four indicators that should tell you why your EDI is broken, and what you can do about it.
- EDI does not connect to your back end systems
- EDI documents are not automatically integrated into your back-office applications, such as an ERP
- Custom scripts that require constant maintenance
- Constantly needing to update in-house custom scripts
- Manual interventions or actions
- Manual intervention is needed for an actual EDI transaction integration
- Your EDI Implementation hasn't progressed
- EDI implementation issues have caused you continual headaches connecting to EDI trading partners
If any of this sounds familiar and you can't support end-to-end EDI integration, fear not, because there is a remedy! There are steps you can take immediately to become more agile, flexible, and easy to do business with than ever before. For instance:
1. API and EDI on one integration platform
It is no longer an either-or question. In order for your business to grow and modernize, you must be able to support EDI and APIs on the same integration platform. EDI and APIs are complementary to each other, that's why you need both working together for you. API integration augments EDI and provides a deeper context to B2B integrations within your business ecosystem.
2. Support for batch and real-time actions
Businesses need end-to-end visibility across the extended supply chain in order to bring real-time API and batch EDI together onto the same EDI interface, so all stakeholders both inside and outside the business can see how all of the integrations are performing. This makes your business highly flexible and integration simpler, easier, faster, and more reliable.
3. Application connectors for direct integration
Often, businesses struggle to integrate different parts of their business ecosystem, whether that might be enterprise applications, SaaS, or EDI. That doesn't have to be the case, however, through a unified, minimally complex technique. Application integration connectors allow enterprises to expand and evolve, something every organization needs to be able to do in 2024.
4. Integration system orchestration and automation
Businesses that can quickly design, configure, and orchestrate integrations with popular and widely used applications and marketplaces make saying "Yes' to prospective customers instead of "No' much easier. Imagine having the technology to dynamically orchestrate end-to-end business processes and integrate data flows to any cloud or on-premise location - that's what a modernized integration platform can and will do for you.
Expanding Your EDI Knowledge: Three Key Questions Answered
While the blog post provides a solid introduction to EDI integration, it's natural to have further questions as you consider its implementation for your business. Here, we address three common inquiries that can help you navigate your EDI journey:
1. What are the different types of EDI transactions that can be integrated?
EDI encompasses a vast range of standardized transactions used for various business processes. Some of the most common types include:
- Purchase orders and invoices: Streamline communication and automate processes related to ordering and payment.
- Shipping notifications and confirmations: Enhance visibility and efficiency throughout the supply chain by electronically exchanging shipment details.
- Inventory inquiries and confirmations: Improve inventory management and collaboration with trading partners by receiving real-time updates.
- Functional acknowledgements: Confirm receipt and validity of data transmissions, ensuring smooth information exchange.
This is not an exhaustive list, and depending on your industry and specific needs, you may utilize a variety of other EDI transactions to streamline your business operations. Consulting with an EDI specialist can help you identify the most relevant transactions for your unique situation.
2. How can I ensure a smooth EDI integration process with minimal disruption to my business operations?
A successful EDI integration requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key steps to ensure a smooth transition:
- Clearly define your goals and requirements: Identify the specific areas where EDI integration will offer the most benefit and determine the data you intend to exchange electronically.
- Collaborate with your trading partners: Ensure they are compatible with your chosen EDI solution and agree on communication standards and data formats.
- Choose the right EDI provider: Select a provider with experience in your industry and a proven track record of successful implementations.
- Invest in training for your team: Familiarize your staff with the new system and processes to ensure smooth adoption and efficient use of EDI.
By proactively addressing these aspects, you can minimize potential disruptions and pave the way for a successful and beneficial EDI implementation.
3. What are the ongoing maintenance requirements after implementing EDI integration?
Maintaining a robust EDI system requires ongoing efforts to ensure its continued effectiveness. Some key maintenance tasks include:
- Regular monitoring and troubleshooting: Regularly monitor for errors and address any issues promptly to maintain data integrity and system functionality.
- Software updates and security patches: Stay up-to-date with the latest software versions and security patches from your EDI provider to ensure optimal performance and mitigate security risks.
- Trading partner management: Maintain communication with your trading partners and adapt to any changes in their EDI systems or requirements.
By dedicating resources to ongoing maintenance, you can ensure your EDI system continues to operate smoothly and deliver long-term value for your business.
Remember, EDI integration can be a powerful tool for enhancing your business efficiency and competitiveness. By addressing these additional questions and actively planning your implementation process, you can set your business up for success in the world of electronic data interchange.
So, if your B2B integration is broken...
If your current integration strategy does not support end-to-end EDI integration, you ought to embrace a modern integration platform that transforms an EDI document and puts it into your back-end system to complete its lifecycle B2B transaction. EDI and API on the same platform will help you leverage integration for the benefit of not just your company, but your entire business ecosystem.
There are other smart moves you can make to fix B2B integration at your company, and we'll be writing about them in future blogs. But if you want the full story now, download our booklet, 'Your B2B Integration Strategy is Broken - Here's What to Do About It'.
Want to discuss your unique EDI needs / current pain-points? We're happy to chat.

About Cleo
Watch a Demo

Comprehensive Guide to Gaining B2B Control

Duraflame Case Study